Page 26 - GPD-3-2
P. 26
Gene & Protein in Disease Review of CAR-T in ADs
A B C
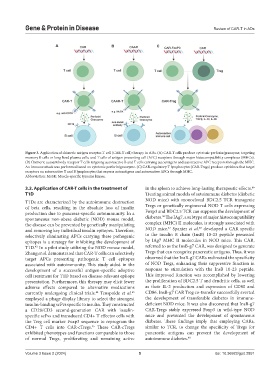
Figure 3. Application of chimeric antigen receptor-T cell (CAR-T cell) therapy in ADs. (A) CAR-T cells produce cytotoxic perforin/granzyme, targeting
memory B cells or long-lived plasma cells, and T cells of antigen-presenting cell (APC) receptors through major histocompatibility complexes (MHCs).
(B) Chimeric autoantibody receptor T cells targeting autoreactive B and T cells carrying autoantigens and autoreactive APC receptors through the MHC.
An immune attack was performed based on cytotoxic perforin/granzyme. (C) CAR-regulatory T lymphocytes (CAR-Tregs) produce cytokines that target
receptors on autoreactive T and B lymphocytes that express autoantigens and autoreactive APCs through MHC.
Abbreviation: MuSK: Muscle-specific tyrosine kinase.
46
3.2. Application of CAR-T cells in the treatment of in the spleen to achieve long-lasting therapeutic effects.
T1D Treating animal models of autoimmune diabetes (diabetic
T1Ds are characterized by the autoimmune destruction NOD mice) with monoclonal BDC2.5 TCR transgenic
of beta cells, resulting in the absolute loss of insulin Tregs or genetically engineered NOD T cells expressing
production due to pancreas-specific autoimmunity. In a Foxp3 and BDC2.5 TCR can suppress the development of
36
spontaneous non-obese diabetic (NOD) mouse model, diabetes. The IAg7, a subtype of major histocompatibility
the disease can be prevented by genetically manipulating complex (MHC) II molecules, is strongly associated with
48
47
and removing key individual insulin epitopes. Therefore, NOD mice. Spanier et al. developed a CAR specific
selectively eliminating APCs carrying these pathogenic to the insulin B chain (InsB) 10-23 peptide presented
epitopes is a strategy for inhibiting the development of by IAg7 MHC II molecules in NOD mice. This CAR,
T1D. In a pilot study utilizing the NOD mouse model, referred to as the InsB-g7 CAR, was designed to generate
43
Zhang et al. demonstrated that CAR-T cells can selectively Tregs that can recognize pancreatic antigens. Thus, it was
target APCs presenting pathogenic T cell epitopes observed that the InsB-g7 CARs redirected the specificity
associated with autoimmunity. This study aided in the of NOD Tregs, enhancing their suppressive function in
development of a successful antigen-specific adoptive response to stimulation with the InsB 10-23 peptide.
cell treatment for T1D based on disease-relevant epitope This improved function was accomplished by lowering
presentation. Furthermore, this therapy may elicit fewer the proliferation of BDC2.5 T and dendritic cells, as well
adverse effects compared to alternative medications as their IL-2 production and expression of CD80 and
currently undergoing clinical trials. Tenspolde et al. CD86. InsB-g7 CAR Treg co-transfer successfully averted
44
45
employed a phage display library to select the strongest the development of transferable diabetes in immune-
insulin-binding scFvs specific to insulin. They constructed deficient NOD mice. It was also discovered that InsB-g7
a CD28/CD3 second-generation CAR with insulin- CAR-Tregs stably expressed Foxp3 in wild-type NOD
specific scFvs and transduced CD4+ T effector cells with mice and prevented the development of spontaneous
the Treg cell marker Foxp3 sequence to reprogram the diabetes. These findings imply that employing CARs,
CD4+ T cells into CAR-cTregs. These CAR-cTregs similar to TCR, to change the specificity of Tregs for
45
exhibited phenotypes and functions comparable to those pancreatic antigens can prevent the development of
of normal Tregs, proliferating and remaining active autoimmune diabetes. 48
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/gpd.2851