Page 78 - GPD-3-4
P. 78
Gene & Protein in Disease Interleukins-1β, interleukin-8, and the SARS-CoV-2
RT-PCR and the patient’s vaccination status, as described chills (P < 0.001), conjunctival congestion (P < 0.001),
in Table 1. abdominal pain (P = 0.002), dyspnea (P < 0.001), and oxygen
saturation <95% (P < 0.001). However, no statistically
3.2. IL-1β, IL-8, and IL-1RN expression
significant differences were observed in the frequency
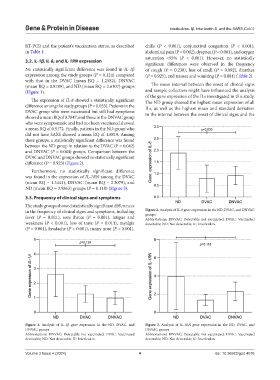
No statistically significant difference was found in IL-1β of cough (P = 0.238), loss of smell (P = 0.092), diarrhea
expression among the study groups (P = 0.124) compared (P = 0.925), and nausea and vomiting (P = 0.084) (Table 2).
with that in the DVAC (mean RQ = 1.2582), DNVAC
(mean RQ = 0.9789), and ND (mean RQ = 2.6107) groups The mean interval between the onset of clinical signs
(Figure 1). and sample collection might have influenced the analysis
of the gene expression of the ILs investigated in this study.
The expression of IL-8 showed a statistically significant The ND group showed the highest mean expression of all
difference among the study groups (P = 0.033). Patients in the ILs, as well as the highest mean and standard deviation
DVAC group who were vaccinated but still had symptoms in the interval between the onset of clinical signs and the
showed a mean RQ of 0.7847, and those in the DNVAC group
who were symptomatic and had not been vaccinated showed
a mean RQ of 0.9172. Finally, patients in the ND group who
did not have SARS showed a mean RQ of 1.8819. Among
these groups, a statistically significant difference was found
between the ND group in relation to the DVAC (P = 0.042)
and DNVAC (P = 0.044) groups. Comparison between the
DVAC and DNVAC groups showed no statistically significant
difference (P = 0.923) (Figure 2).
Furthermore, no statistically significant difference
was found in the expression of IL-1RN among the DVAC
(mean RQ = 1.3441), DNVAC (mean RQ = 2.3079), and
ND (mean RQ = 3.9863) groups (P = 0.118) (Figure 3).
3.3. Frequency of clinical signs and symptoms
The study groups showed statistically significant differences
in the frequency of clinical signs and symptoms, including Figure 2. Analysis of IL-8 gene expression in the ND, DVAC, and DNVAC
fever (P = 0.021), sore throat (P = 0.001), fatigue and groups
Abbreviations: DNVAC: Detectable not vaccinated; DVAC: Vaccinated
weakness (P < 0.001), loss of taste (P = 0.014), myalgia detectable; ND: Not detectable; IL: Interleukin.
(P < 0.001), headache (P < 0.001), runny nose (P < 0.001),
Figure 1. Analysis of IL-1β gene expression in the ND, DVAC, and Figure 3. Analysis of IL-1RN gene expression in the ND, DVAC, and
DNVAC groups DNVAC groups
Abbreviations: DNVAC: Detectable not vaccinated; DVAC: Vaccinated Abbreviations: DNVAC: Detectable not vaccinated; DVAC: Vaccinated
detectable; ND: Not detectable; IL: Interleukin. detectable; ND: Not detectable; IL: Interleukin.
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4076