Page 62 - GPD-4-1
P. 62
Gene & Protein in Disease rs670 SNP in APOA1 gene
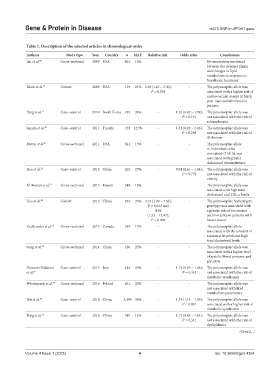
Table 1. Description of the selected articles in chronological order
Authors Study type Year Country n MAF Relative risk Odds ratio Conclusions
Liu et al. 50 Cross-sectional 2009 USA 861 16% - - No association was found
between the polymorphism
and changes in lipid
metabolism in response to
fenofibrate treatment
Block et al. 13 Cohort 2009 USA 129 21% 2.40 (1.07 – 5.40); - The polymorphic allele was
P = 0.034 associated with a higher risk of
cardiovascular events in black
post-myocardial infarction
patients
Yang et al. 11 Case–control 2010 South Korea 185 24% - 1.32 (0.87 – 1.99); The polymorphic allele was
P = 0.191 not associated with the risk of
schizophrenia
Smach et al. 12 Case–control 2011 Tunisia 173 22.5% - 1.31 (0.82 – 2.06); The polymorphic allele was
P = 0.258 not associated with the risk of
Alzheimer
Mattei et al. 51 Cross-sectional 2011 USA 821 15% - - The polymorphic allele
in individuals who
consumed<31% fat was
associated with greater
abdominal circumference
Hsu et al. 52 Case–control 2013 China 262 27% - 0.94 (0.61 – 1.44); The polymorphic allele was
P = 0.774 not associated with the risk of
obesity
Al-Bustan et al. 53 Cross-sectional 2013 Kuwait 549 19% - - The polymorphic allele was
associated with high total
cholesterol and LDL-c levels
Hsu et al. 48 Cohort 2013 China 223 35% 3.12 (1.29 – 7.56); - The polymorphic homozygote
P = 0.012 and genotype was associated with
4.36 a greater risk of recurrence
(1.52 – 12.47); and mortality in patients with
P = 0.006 breast cancer
Rudkowska et al. 54 Cross-sectional 2013 Canada 553 17% - - The polymorphic allele
associated with the amount of
saturated fat predicted high
total cholesterol levels
Song et al. 55 Cross-sectional 2014 China 180 27% - - The polymorphic allele was
associated with a higher level
of systolic blood pressure and
glycemia
Hosseini-Esfahani Case–control 2015 Iran 414 29% - 1.11 (0.85 – 1.46); The polymorphic allele was
et al. 56 P = 0.443 not associated with the risk of
metabolic syndromes
Włodarczyk et al. 57 Cross-sectional 2016 Poland 621 22% - - The polymorphic allele was
not associated with lipid
metabolism parameters
Wu et al. 10 Case–control 2016 China 3,340 26% - 1.31 (1.14 – 1.50); The polymorphic allele was
P < 0.001 associated with a higher risk of
metabolic syndromes
Feng et al. 58 Case–control 2016 China 340 14% - 1.17 (0.84 – 1.64); The polymorphic allele was
P = 0.341 not associated with the risk of
dyslipidemia
(Cont'd...)
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 4 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4354