Page 143 - GPD-4-2
P. 143
Gene & Protein in Disease BCL11A targets and chromatin binding patterns
A
B
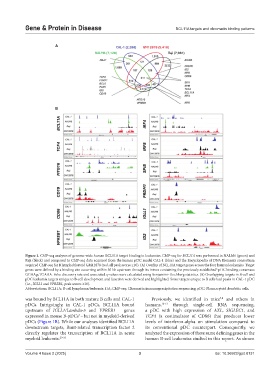
Figure 1. ChIP-seq analyses of genome-wide human BCL11A target binding in leukemias. ChIP-seq for BCL11A was performed in NALM6 (green) and
Raji (black) and compared to ChIP-seq data acquired from the human pDC model CAL-1 (blue) and the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements consortium
acquired ChIP-seq for B lymphoblastoid GM12878 (red, all peak scores ≥10). (A) Overlap of BCL11A target genes across the four human leukemias. Target
8
genes were defined by a binding site occurring within 50 kb upstream through its intron containing the previously established pDC binding consensus
GGAAgcTGAAA. False discovery rate and associated q-values were calculated using Benjamini–Hochberg statistics. (B) Overlapping targets in B-cell and
pDC leukemia targets unique to B-cell development and function were derived and highlighted. Some targets unique to B cells had peaks in CAL-1 pDC
(i.e., IGLL1 and VPREB1, peak scores ≥10).
Abbreviations: BCL11A: B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 11A; ChIP-seq: Chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing; pDC: Plasmacytoid dendritic cells.
was bound by BCL11A in both mature B cells and CAL-1 Previously, we identified in mice and others in
7,8
pDCs. Intriguingly, in CAL-1 pDCs, BCL11A bound humans, 10-12 through single-cell RNA sequencing,
upstream of IGLL1/Lambda-5 and VPREB1 – genes a pDC with high expression of AXL, SIGLEC1, and
expressed in mouse B-pDCs –but not in myeloid-derived TCF4 (a costimulator of CD86) that produces lower
7
pDCs (Figure 1B). While our analyses identified BCL11A levels of interferon-alpha on stimulation compared to
downstream targets, Runt-related transcription factor 2 its conventional pDC counterpart. Consequently, we
directly regulates the transcription of BCL11A in acute analyzed the expression of these same defining genes in the
myeloid leukemia. 29-31 human B-cell leukemias studied in this report. As shown
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 3 doi: 10.36922/gpd.8131