Page 72 - GPD-4-3
P. 72
Gene & Protein in Disease Cullin family members as biomarkers in KIRC
2.6. TIMER database analysis CUL4A, CUL4B, and CUL9, whereas CUL3, CUL5, and
TIMER (https://cistrome.shinyapps.io/timer/) is a web- CUL7 were downregulated in kidney cancer. CUL1
based tool aimed at enabling in-depth assessment of and CUL2 mRNA levels were overexpressed 2.172-fold
immune cell infiltration and its clinical significance. We and 2.617-fold, respectively, in Wilms’ tumor compared to
18
20
19
analyzed the expression levels of cullin proteins and their healthy control tissues. According to Jones et al., CUL3
associations with tumor purity and immune cell infiltration expression was reduced in clear cell RCC (CCRCC; relative
in KIRC, including B cells, macrophages, neutrophils, change = −2.340) and renal pelvis urothelial carcinoma
CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, and dendritic cells. (relative change = −2.133). It was also downregulated in renal
+
+
oncocytoma (relative change = −4.876) and chromophobe
19
3. Results RCC (relative change = −5.238) in the Yusenko et al.
dataset. In the same dataset, CUL4A was also shown to be
3.1. Transcriptional expression of cullin genes in higher in Wilms’ tumor (relative change = 4.757) compared
patients with kidney cancer to control samples. When compared to healthy controls,
19
The ONCOMINE database was employed to probe the Beroukhim et al. discovered that in hereditary CCRCC,
21
differential expression patterns of cullins in patients with the expression of CUL4B mRNA was heightened (relative
kidney cancer. Initially, we assessed the transcriptional change = 2.192). CUL5 expression was downregulated in
profiles in both malignant and healthy tissues. Our renal oncocytoma (relative change = −3.055), CCRCC
analysis revealed that the expression of all nine cullin (relative change = −3.264), and renal pelvis urothelial
family genes (CUL1 – 9) varied significantly in renal carcinoma (relative change = 2.548) in a study by Jones
cancer (Figure 1). Specifically, ONCOMINE analysis et al. CUL5 expression was downregulated in Wilms tumor
20
showed elevated mRNA expression of CUL1, CUL2, (relative change = −2.094), according to Cutcliffe et al.
22
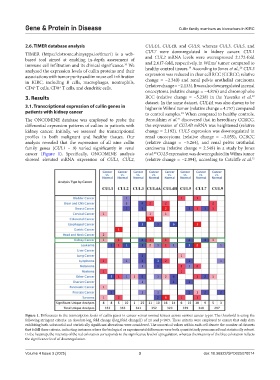
Figure 1. Differences in the transcription levels of cullin genes in cancer versus normal tissues across various cancer types. The threshold is using the
following stringent criteria: an absolute log fold change (|log (fold change)|) of ≥1 and p<0.05. These criteria were employed to ensure that only data
2
2
exhibiting both substantial and statistically significant alterations were considered. The numerical values within each cell denote the number of datasets
that fulfill these criteria, indicating instances where the biological or experimental differences were both quantitatively pronounced and statistically robust.
In the heatmap, the intensity of the red coloration corresponds to the significance level of upregulation, whereas the intensity of the blue coloration reflects
the significance level of downregulation.
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 3 doi: 10.36922/GPD025070014