Page 37 - GTM-2-1
P. 37
Global Translational Medicine Stem cells in aortic aneurysm
at the cellular and molecular levels. However, there are
several limitations and unresolved issues. For example,
AAA is mostly induced by Ang II, which limits research
on inflammatory mechanisms. Research of TAA is most
focused on genetic models. In the occurrence, growth
and rupture of AA, more studies have focused on the
developmental stage rather than defining the entire disease
process . Therefore, new models and more innovative
[7]
approaches are needed to study AA.
As for the role of stem cells in AA, the current research
may suggest that they play a crucial role in the occurrence
and development of AA. But more importantly, the
clinical treatment of AA by utilizing the differentiation
and proliferation ability of stem cells has a good prospect.
EPC will be mainly used for the prediction and prognostic
evaluation of AA, but at present, it is mainly used to
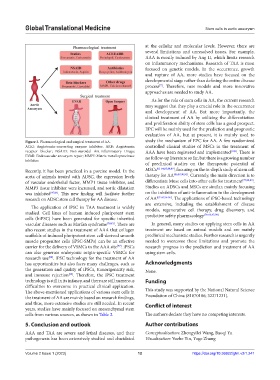
Figure 3. Pharmacological and surgical treatment of AA. study the mechanism of EPC for AA. A few randomized
ACEI: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB: Angiotensin controlled clinical studies of MSCs in the treatment of
receptor blocker; NSAID: Non-steroidal Ant-inflammatory Drugs; AAA have been registered and implemented [109] . There is
EVAR: Endovascular aneurysm repair; MMPI: Matrix metalloproteinase no follow-up literature so far, but there is a growing number
inhibitor.
of preclinical studies on the therapeutic potential of
Recently, it has been practiced in a porcine model. In the MSCs [61-64,85,88,89] , focusing on the in-depth study of stem cell
aorta of animals treated with ADSC, the expression levels therapy for AA [86,87,90,91] . Currently, the main direction is to
of vascular endothelial factor, MMP1 tissue inhibitor, and differentiate Muse cells into other cells for treatment [77,92,93] .
MMP3 tissue inhibitor were increased, and aortic dilatation Studies on ADSCs and MSCs are similar, mainly focusing
was inhibited [95,96] . This new finding will facilitate further on the inhibition of anti-inflammation in the development
research on ADSC stem cell therapy for AA disease. of AA [67-69,94-96] . The applications of iPSC-based technology
are extensive, including the establishment of disease
The application of iPSC in TAA treatment is widely models, regenerative cell therapy, drug discovery, and
studied. Cell lines of human induced pluripotent stem predictive safety pharmacology [78-83,97,98]
cells (hiPSC) have been generated for specific inherited
vascular diseases such as Marfan syndrome [78,81] . There are In general, many studies on applying stem cells in AA
also recent studies in the treatment of AAA that collagen treatment are based on animal models and are mainly
scaffolds of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived smooth preclinical mechanistic studies. Further research is urgently
muscle progenitor cells (iPSC-SMPs) can be an effective needed to overcome these limitations and promote the
carrier for the delivery of VSMCs to the AAA site . iPSCs research progress in the prediction and treatment of AA
[97]
can also generate embryonic origin-specific VSMCs for using stem cells.
research use . iPSC technology for the treatment of AA
[98]
has opportunities but also faces many challenges, such as Acknowledgments
the generation and quality of iPSCs, tumorigenicity risk, None.
and immune rejection . Therefore, the iPSC treatment
[99]
technology is still in its infancy, and there are still numerous Funding
difficulties to overcome in practical clinical application.
The above-mentioned applications of various stem cells in This study was supported by the National Natural Science
the treatment of AA are mainly based on research findings, Foundation of China (81870186; 32271231).
and thus, more extensive studies are still needed. In recent Conflict of interest
years, studies have mainly focused on mesenchymal stem
cells from various sources, as shown in Table 2. The authors declare they have no competing interests.
5. Conclusion and outlook Author contributions
AAA and TAA are severe and lethal diseases, and their Conceptualization: Zhengyilei Wang, Baoqi Yu
pathogenesis has been extensively studied and elucidated Visualization: Yuzhe Yin, Yuge Zhang
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 12 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v2i1.241