Page 57 - GTM-2-1
P. 57
Global Translational Medicine ABE gene therapy for CVDs
A
B
C
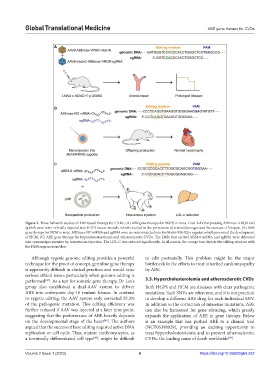
Figure 2. Three hallmark studies of ABE-based therapy for CVDs. (A) ABE gene therapy for HGPS in mice. Dual AAV9 expressing ABEmax-VRQR and
sgRNA were retro-orbitally injected into HGPS mouse models, which resulted in the prevention of arterial damages and the increase of lifespan. (B) ABE
gene therapy for HCM in mice. ABEmax-NG mRNA and sgRNA were co-microinjected into the Myh6-R404Q/+ zygotes, which prevented the development
of HCM. (C) ABE gene therapy for hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerotic CVDs. The LNPs that carried ABE8.8 mRNA and sgRNA were delivered
into cynomolgus monkey by intravenous injection. The LDL-C was reduced significantly. In all panels, the orange box depicts the editing window with
the PAM sequences in blue.
Although zygotic genome editing provides a powerful to edit postnatally. This problem might be the major
technique for the proof of concept, germline gene therapy bottleneck in the efforts to treat inherited cardiomyopathy
is apparently difficult in clinical practices and would raise by ABE.
serious ethical issues particularly when genome editing is
performed . As a test for somatic gene therapy, Dr Lan’s 3.3. Hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerotic CVDs
[47]
group also established a dual-AAV system to deliver Both HGPS and HCM are diseases with clear pathogenic
ABE into embryonic day-16 mutant fetuses. In contrast mutations. Such SNVs are often rare, and it is not practical
to zygotic editing, the AAV system only corrected 25.3% to develop a different ABE drug for each individual SNV.
of the pathogenic mutation. This editing efficiency was In addition to the correction of missense mutations, ABE
further reduced if AAV was injected at a later time point, can also be harnessed for gene silencing, which greatly
suggesting that the performance of ABE heavily depends expands the application of ABE in gene therapy. Below
on the developmental stage of the heart . The authors is an example that has pushed ABE to a clinical trial
[46]
argued that the success of base editing required active DNA (NCT05398029), providing an exciting opportunity to
replication or cell cycle. Thus, mature cardiomyocytes, as treat hypercholesterolemia and to prevent atherosclerotic
a terminally differentiated cell type , might be difficult CVDs, the leading cause of death worldwide .
[49]
[48]
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.232