Page 23 - GTM-2-3
P. 23
Global Translational Medicine Critical roles for BRD4 identified in cancer
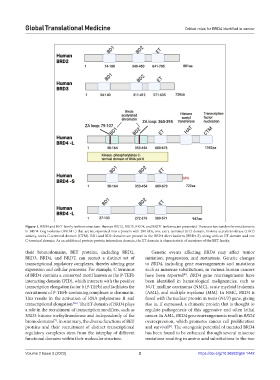
Figure 1. BRD4 and BET family isoform structure. Human BRD2, BRD3, BRD4, and BRDT isoforms are presented. There are two tandem bromodomains
in BRD4 long isoforms (BRD4-L) that are incorporated into a protein with 200 kDa, one extra-terminal (ET) domain, histone acetyltransferase (HAT)
activity, and a C-terminal domain (CTM). BD1 and BD2 domains are present in the BRD4 short isoform (BRD4-S), along with an ET domain and one
C-terminal domain. As an additional protein-protein interaction domain, the ET domain is characteristic of members of the BET family.
their bromodomains, BET proteins, including BRD2, Genetic events affecting BRD4 may affect tumor
BRD3, BRD4, and BRDT, can recruit a distinct set of initiation, progression, and metastasis. Genetic changes
transcriptional regulatory complexes, thereby altering gene to BRD4, including gene rearrangements and mutations
expression and cellular processes. For example, C terminus such as missense substitutions, in various human cancers
of BRD4 contains a conserved motif known as the P-TEFb have been reported . BRD4 gene rearrangements have
[8]
interacting domain (PID), which interacts with the positive been identified in hematological malignancies, such as
transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) and facilitates the NUT midline carcinoma (NMC), acute myeloid leukemia
recruitment of P-TEFb-containing complexes to chromatin. (AML), and multiple myeloma (MM). In NMC, BRD4 is
This results in the activation of RNA polymerase II and fused with the nuclear protein in testis (NUT) gene, giving
transcriptional elongation [5,6] . The ET domain of BRD4 plays rise to, if expressed, a chimeric protein that is thought to
a role in the recruitment of transcription modifiers, such as regulate pathogenesis of this aggressive and often lethal
NSD3 histone methyltransferase and independently of the cancer. In AML, BRD4 gene rearrangements result in BRD4
bromodomains . In summary, the diverse functions of BET overexpression, which promotes cancer cell proliferation
[7]
proteins and their recruitment of distinct transcriptional and survival . The oncogenic potential of mutated BRD4
[6]
regulatory complexes stem from the interplay of different has been found to be enhanced through several missense
functional domains within their molecular structure. mutations resulting in amino acid substitutions in the two
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 2 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.1442