Page 27 - GTM-2-3
P. 27
Global Translational Medicine Critical roles for BRD4 identified in cancer
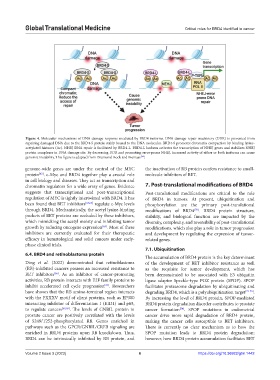
Figure 4. Molecular mechanisms of DNA damage response mediated by BRD4 isoforms. DNA damage repair machinery (DDR) is prevented from
repairing damaged DNA due to the BRD4-S protein stably bound to the DNA molecules. BRD4-S promotes chromatin compaction by binding lysine-
acetylated histones (Ac). NHEJ DNA repair is facilitated by BRD4-L. BRD4-L isoform activates the transcription of NHEJ genes and stabilizes NHEJ
protein complexes in DNA damage site. By decreasing DDR and promoting error-prone NHEJ, increased activity of either or both isoforms can cause
[24]
genomic instability. This figure is adapted from Drumond-Bock and Bieniasz .
genome-wide genes are under the control of the MYC the inactivation of RB protein confers resistance to small-
protein . c-Myc and BRD4 together play a crucial role molecule inhibitors of BET.
[62]
in cell biology and diseases. They act as transcription and
chromatin regulators for a wide array of genes. Evidence 7. Post-translational modifications of BRD4
suggests that transcriptional and post-transcriptional Post-translational modifications are critical to the role
regulation of MYC is tightly intertwined with BRD4. It has of BRD4 in tumors. At present, ubiquitination and
been found that BET inhibitors [63,64] regulate c-Myc levels phosphorylation are the primary post-translational
through BRD4. Mechanistically, the acetyl lysine-binding modifications of BRD4 . BRD4 protein structure,
[70]
pockets of BET proteins are occluded by these inhibitors, stability, and biological function are impacted by the
which mimicking the acetyl moiety and inhibiting tumor diversity, complexity, and reversibility of post-translational
growth by reducing oncogene expression . Most of these modifications, which also play a role in tumor progression
[65]
inhibitors are currently evaluated for their therapeutic and development by regulating the expression of tumor-
efficacy in hematological and solid cancers under early- related genes.
phase clinical trials.
7.1. Ubiquitination
6.4. BRD4 and retinoblastoma protein
The accumulation of BRD4 protein is the key determinant
Ding et al. (2022) demonstrated that retinoblastoma of the development of BET inhibitor resistance as well
(RB)-inhibited cancers possess an increased resistance to as the requisite for tumor development, which has
BET inhibitors . As an inhibitor of cancer-promoting been demonstrated to be associated with E3 ubiquitin
[66]
activities, RB protein interacts with E2F family proteins to ligase adaptor Speckle-type POZ protein (SPOP). SPOP
inhibit accelerated cell cycle progression . Researchers facilitates proteasome degradation by ubiquitinating and
[67]
have shown that the RB amino-terminal region interacts degrading BRD4, which is a polyubiquitination target [71-73] .
with the FXXXV motif of client proteins, such as EP300 By increasing the level of BRD4 protein, SPOP-mediated
interacting inhibitor of differentiation 1 (EID1) and p65, BRD4 protein degradation disorder contributes to prostate
to regulate cancers [68,69] . The levels of GNBIL protein in cancer formation . SPOP mutations in endometrial
[74]
prostate cancer are positively correlated with the levels cancer drive more rapid degradation of BRD4 protein,
of S249/T252-phosphorylated RB. Genes enriched in making the cancer cells susceptible to BET inhibitors.
pathways such as the GPCR/GNBIL/CREB signaling are There is currently no clear mechanism as to how the
enriched in BRD4 proteins upon RB knockdown. Thus, SPOP mutation leads to BRD4 protein degradation;
BRD4 can be intrinsically inhibited by RB protein, and however, how BRD4 protein accumulation facilitates BET
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.1442