Page 25 - GTM-2-3
P. 25
Global Translational Medicine Critical roles for BRD4 identified in cancer
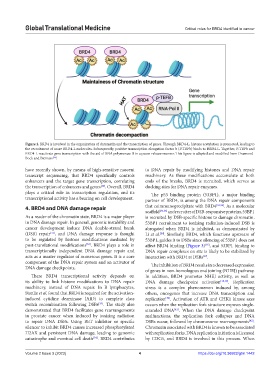
Figure 2. BRD4 is involved in the organization of chromatin and the transcription of genes. Through BRD4-L, histone acetylation is promoted, leading to
the recruitment of more BRD4-L molecules. Subsequently, positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) binds to BRD4-L. Together, P-TEFb and
BRD4-L reactivate gene transcription with the aid of RNA polymerase II in a pause-release manner. This figure is adapted and modified from Drumond-
[24]
Bock and Bieniasz .
have recently shown, by means of high-sensitive nascent to DNA repair by modifying histones and DNA repair
transcript sequencing, that BRD4 specifically controls machinery. As these modifications accumulate at both
enhancers and the target gene transcription, correlating ends of the breaks, BRD4 is recruited, which serves as
the transcription of enhancers and genes . Overall, BRD4 docking sites for DNA repair enzymes.
[30]
plays a critical role in transcription regulation, and its The p53 binding protein (53BP1), a major binding
transcriptional activity has a bearing on cell development. partner of BRD4, is among the DNA repair components
4. BRD4 and DNA damage repair that coimmunoprecipitate with BRD4 [33,34] . As a molecular
scaffold [35,36] and recruiter of DSB-responsive proteins, 53BP1
As a reader of the chromatin state, BRD4 is a major player is recruited by DSB-specific histone to damage chromatin.
in DNA damage repair. In general, genomic instability and 53BP1 recruitment to ionizing radiation-induced DSB is
cancer development induce DNA double-strand break abrogated when BRD4 is inhibited, as demonstrated by
(DSB) repair , and DNA damage response is thought Li et al. . Similarly, BRD4, which functions upstream of
[31]
[34]
to be regulated by histone modifications mediated by 53BP1, guides it to DSBs since silencing of 53BP1 does not
post-translational modifications . BRD4 plays a role in affect BRD4 binding (Figure 3) , and 53BP1 binding to
[32]
[35]
transcriptionally independent DNA damage repair and DNA repair complexes on site is likely to be stabilized by
acts as a master regulator of numerous genes. It is a core interaction with BRD4 at DSBs .
[37]
component of the DNA repair system and an activator of The inhibition of BRD4 results in a decreased expression
DNA damage checkpoints.
of genes in non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway.
There BRD4 transcriptional activity depends on In addition, BRD4 promotes NHEJ activity, as well as
its ability to link histone modifications to DNA repair DNA damage checkpoint activation [38,39] . Replication
machinery, instead of DNA repair. In B lymphocytes, stress is a complex phenomenon induced by, among
Stanlie et al. found that BRD4 is required for the activation- others, oncogenes that increase DNA transcription and
induced cytidine deaminase (AID) to complete class replication . Activation of ATR and CHK1 kinase axes
[40]
switch recombination following DSBs . The study also occurs when the replication fork structure exposes single-
[33]
demonstrated that BRD4 facilitates gene rearrangements stranded DNA . When the DNA damage checkpoint
[41]
in prostate cancer when induced by ionizing radiation malfunctions, the replication fork collapses and DNA
to repair DNA DSBs. Using BET inhibitor or specific DSBs occur, followed by chromosome rearrangements .
[42]
silencer to inhibit BRD4 causes increased phosphorylated Chromatin associated with BRD4 is known to be associated
H2AX and persistent DNA damage, leading to genomic with replication forks. DNA replication initiation is licensed
catastrophe and eventual cell death . BRD4 contributes by CDC6, and BRD4 is involved in this process. When
[34]
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.1442