Page 26 - GTM-2-3
P. 26
Global Translational Medicine Critical roles for BRD4 identified in cancer
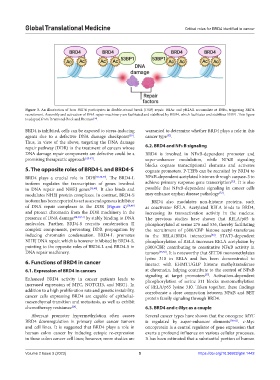
Figure 3. An illustration of how BRD4 participates in double-strand break (DSB) repair. H4Ac and γH2AX accumulate at DSBs, triggering BRD4
recruitment. Assembly and activation of DNA repair machinery are facilitated and stabilized by BRD4, which facilitates and stabilizes 53BP1. This figure
[24]
is adapted from Drumond-Bock and Bieniasz .
BRD4 is inhibited, cells can be exposed to stress-inducing warranted to determine whether BRD4 plays a role in this
agents due to a defective DNA damage checkpoint . cancer type .
[52]
[39]
Thus, in view of the above, targeting the DNA damage
repair pathway (DDR) in the treatment of cancers whose 6.2. BRD4 and NFκB signaling
DNA damage repair components are defective could be a BRD4 is involved in NFκB-dependent promoter and
promising therapeutic approach [43-47] . super-enhancer modulation, while NFκB signaling
blocks cognate transcriptional elements and activates
5. The opposite roles of BRD4-L and BRD4-S cognate promoters. P-TEFb can be recruited by BRD4 to
BRD4 plays a crucial role in DDR [34,48,49] . The BRD4-L NFκB-dependent acetylated histones through caspase-3 to
[53]
isoform regulates the transcription of genes involved achieve primary response gene transcription . It is also
in DNA repair and NHEJ genes [33,48] . It also binds and possible that NFκB-dependent signaling in cancer cells
[52]
modulates NHEJ protein complexes. In contrast, BRD4-S may enhance orphan disease pathology .
isoform has been reported to act as an endogenous inhibitor BRD4 also modulates non-histone proteins, such
of DNA repair complexes in the DDR (Figure 4) [38,48] as coactivator RELA. Acetylated RELA binds to BRD4,
and protect chromatin from the DDR machinery in the increasing its transactivation activity in the nucleus.
presence of DNA damage [48,50,51] by stably binding to DNA The previous studies have shown that RELA/p65 is
molecules. Further, BRD4-S recruits condensation II phosphorylated at serine 276 and 536, thereby facilitating
complex components, preventing DDR propagation by the recruitment of p300/CBP histone acetyl-transferase
inducing chromatin condensation. BRD4-L promotes in the RELA/BRD4 interaction . STAT3-dependent
[54]
NHEJ DNA repair, which is however inhibited by BRD4-S, phosphorylation of RELA increases RELA acetylation by
pointing to the opposite roles of BRD4-L and BRD4-S in p300/CBP, contributing to constitutive NFκB activity in
DNA repair machinery. tumors [55,56] . It is noteworthy that SETD6 monomethylates
lysine 310 in RELA and has been demonstrated to
6. Functions of BRD4 in cancer interact with EHMT1/GLP histone methyltransferase
6.1. Expression of BRD4 in cancers at chromatin, helping contribute to the control of NFκB
signaling at target promoters . Activation-dependent
[57]
Enhanced BRD4 activity in cancer patients leads to phosphorylation of serine 311 blocks monomethylation
increased expression of MYC, NOTCH3, and NRG1. In of RELA/p65 lysine 310. Taken together, these findings
addition to a high proliferation rate and genetic instability, corroborate a close connection between NFκB and BET
cancer cells expressing BRD4 are capable of epithelial- protein family signaling through BRD4.
mesenchymal transition and metastasis, as well as exhibit
chemotherapy resistance . 6.3. BRD4 and c-Myc as a couple
[24]
Aberrant promoter hypermethylation often causes Several cancer types have shown that the oncogene MYC
BRD4 downregulation in primary colon cancer tumors is regulated by super-enhancer elements [58-61] . c-Myc
and cell lines. It is suggested that BRD4 plays a role in oncoprotein is a central regulator of gene expression that
human colon cancer by inducing ectopic re-expression exerts a profound influence on various cellular processes.
in these colon cancer cell lines; however, more studies are It has been estimated that a substantial portion of human
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.1442