Page 78 - GTM-2-3
P. 78
Global Translational Medicine Thromboembolism risk in non-small-cell lung cancer
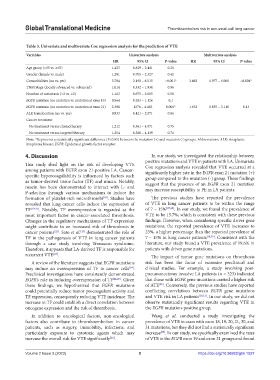
Table 3. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis for the prediction of VTE
Variables Univariate analysis Multivariate analysis
HR 95% Cl P‑value HR 95% Cl P‑value
Age group (<65 vs. ≥65) 1.423 0.829 – 2.441 0.20
Gender (female vs. male) 1.281 0.705 – 2.327 0.41
Comorbidities (no vs. yes) 3.784 2.198 – 6.515 <0.001* 3.462 1.977 – 6.060 <0.001*
TNM Stage (locally advanced vs. advanced) 1.014 0.532 – 1.930 0.96
Number of metastasis (<2 vs. ≥2) 1.163 0.675 – 2.005 0.58
EGFR mutation (no mutation vs. mutation at exon 19) 0.564 0.283 – 1.126 0.1
EGFR mutation (no mutation vs. mutation at exon 21) 2.386 1276 – 4.462 0.006* 1.632 0.855 – 3.116 0.13
ALK translocation (no vs. yes) 0.933 0.421 – 2.071 0.86
Cancer treatment
No treatment versus chemotherapy 1.212 0.361 – 4.071 0.75
No treatment versus targeted therapy 1.254 0.380 – 4.139 0.71
Note: *Represents a statistically significant difference (P<0.05) between the mutation (+) and mutation (-) groups. Abbreviations: ALK: Anaplastic
lymphoma kinase; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor.
4. Discussion In our study, we investigated the relationship between
positive mutations and VTE in patients with LA. Univariate
This study shed light on the risk of developing VTE Cox regression analysis revealed that VTE occurred at a
among patients with EGFR exon 21-positive LA. Cancer- significantly higher rate in the EGFR exon 21 mutation (+)
specific hypercoagulability is influenced by factors such group compared to the mutation (-) group. These findings
as tumor-derived tissue factor (TF) and mucin. Notably, suggest that the presence of an EGFR exon 21 mutation
mucin has been demonstrated to interact with L- and may increase susceptibility to PE in LA patients.
P-selectins through various mechanisms to induce the
formation of platelet-rich microthrombi . Studies have The previous studies have reported the prevalence
[18]
revealed that lung cancer cells induce the expression of of VTE in lung cancer patients to be within the range
TF [19-21] . Notably, TF overexpression is regarded as the of 7 – 15% [27,28] . In our study, we found the prevalence of
most important factor in cancer-associated thrombosis. VTE to be 15.7%, which is consistent with these previous
Changes in the regulatory mechanisms of TF expression findings. However, when considering specific driver gene
might contribute to an increased risk of thrombosis in mutations, the reported prevalence of VTE increases to
cancer patients . Sato et al. demonstrated the role of 23%, a higher percentage than the reported prevalence of
[22]
[23]
TF in the pathogenesis of VTE in lung cancer patients 7 – 15% in lung cancer patients [10,29] . Consistent with the
through a case study involving Trousseau syndrome. literature, our study found a VTE prevalence of 19.6% in
Therefore, it appears that LA-derived TF is responsible for patients with driver gene mutations.
recurrent VTE . The impact of tumor gene mutations on thrombosis
[23]
A review of the literature suggests that EGFR mutations risk has been the focus of extensive preclinical and
may induce an overexpression of TF in cancer cells . clinical studies. For example, a study involving post-
[24]
Preclinical investigations have consistently demonstrated pneumonectomy invasive LA patients (n = 323) indicated
EGFR’s role in inducing overexpression of TF [24,25] . Given that those with EGFR gene mutations carried a higher risk
[29]
these findings, we hypothesized that EGFR mutations of ATE . Conversely, the previous studies have reported
could potentially reduce tumor procoagulant activity and conflicting correlations between EGFR gene mutations
TF expression, consequently reducing VTE incidence. The and VTE risk in LA patients [10,11] . In our study, we did not
increase in TF could establish a direct correlation between observe statistically significant results regarding VTE in
oncogene expression and the risk of thrombosis. the EGFR mutation-positive group.
In addition to oncological factors, non-oncological Wang et al. conducted a study investigating the
factors also contribute to thromboembolism in cancer prevalence of VTE in cases with exon 18, 19, 20, 21, 30, and
patients, such as surgery, immobility, infections, and 31 mutations, but they did not find a statistically significant
particularly exposure to cytotoxic agents which may increase . In our study, we specifically examined the rates
[29]
increase the overall risk for VTE significantly . of VTE in the EGFR exon 19 and exon 21 groups and found
[26]
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.1027