Page 30 - GTM-2-4
P. 30
Global Translational Medicine The research advances in HPV integration
genome are interspersed with cellular DNA, resembling repression of E6/E7 [32,33] . During integration, the early
a Brd4-dependent super-enhancer-like element . The 3’ region of the virus is always deleted completely or
[30]
role of HPV integration in cell transformation and truncated, resulting in the deletion or disruption of E2 and
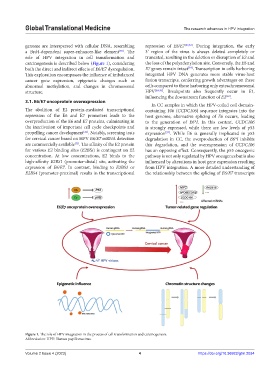
carcinogenesis is described below (Figure 1), considering the loss of the polyadenylation site. Conversely, the E6 and
[34]
both the direct and indirect effects of E6/E7 dysregulation. E7 genes remain intact . Transcription in cells harboring
This exploration encompasses the influence of imbalanced integrated HPV DNA generates more stable virus-host
cancer gene expression, epigenetic changes such as fusion transcripts, conferring growth advantages on these
abnormal methylation, and changes in chromosomal cells compared to those harboring only extrachromosomal
structure. HPV [34-36] . Breakpoints also frequently occur in E1,
influencing the downstream function of E2 .
[12]
3.1. E6/E7 oncoprotein overexpression
In CC samples in which the HPV-coiled coil domain-
The abolition of E2 protein-mediated transcriptional containing 106 (CCDC106) sequence integrates into the
repression of the E6 and E7 promoters leads to the host genome, alternative splicing of E6 occurs, leading
overproduction of the E6 and E7 proteins, culminating in to the generation of E6*I. In this context, CCDC106
the inactivation of important cell cycle checkpoints and is strongly expressed, while there are low levels of p53
propelling cancer development . Notably, screening tests expression . While E6 is generally implicated in p53
[21]
[37]
for cervical cancer based on HPV E6/E7 mRNA detection degradation in CC, the overproduction of E6*I inhibits
are commercially available . The affinity of the E2 protein this degradation, and the overexpression of CCDC106
[31]
for various E2 binding sites (E2BSs) is contingent on E2 has an opposing effect. Consequently, the p53 oncogenic
concentration. At low concentrations, E2 binds to the pathway is not only regulated by HPV oncogenes but is also
high-affinity E2BS1 (promoter-distal) site, activating the influenced by alterations in host gene expression resulting
expression of E6/E7. In contrast, binding to E2BS3 or from HPV integration. A more detailed understanding of
E2BS4 (promoter-proximal) results in the transcriptional the relationship between the splicing of E6/E7 transcripts
Figure 1. The role of HPV integration in the process of cell transformation and carcinogenesis.
Abbreviation: HPV: Human papillomavirus.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.2034