Page 35 - GTM-2-4
P. 35
Global Translational Medicine The research advances in HPV integration
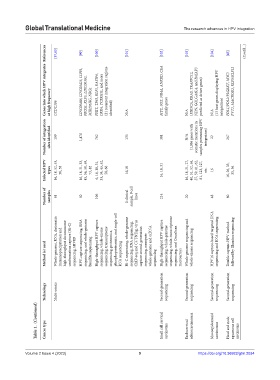
References [37,65] [99] [100] [101] [102] [103] [104] [45] (Cont’d...)
Genes into which HPV integrates at high frequency CCDC106 LINC00486, LINC02425, LLPH, PROS1, KLF5, LINC00392, MIR205HG, NRG1 FHIT, TP63, KLF5, RASSF6, LRBA, TCERG1L, and more (21 recurrent integration regions identified) N/A MYC, SOX, NR4A, ANKRD, CEA family genes N/A (PIK3CA, KRAS, TRAPPC12, NDN, GOLGA6L4, and BAIAP3 predicted as driver genes) N/A (13 host genes displaying HPV integration) PDL1/PDL2/PLGRKT, MYC/ PVT1, MACROD2
Number of integration sites identified 109 1,470 762 135 381 N/A (1,036 genes with somatic mutations in samples presenting HPV integration) 22 267
Infected HPV types 16, 18, 52, 53, 56, 58 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 56, 58, 59, 73, 82 6, 16, 18, 31, 33, 34, 45, 52, 58, 66 16,18 16, 18, 31 16, 18, 21, 27, 40, 51, 52, 56, 57, 59, 61, 62, 81, 123, 127, etc. 16 16, 26, 33, 35, 56
Number of samples 61 50 106 0 clinical sample, 9 cell lines 214 20 48 80
Method (s) used Whole-genome, RNA, chromatin immunoprecipitation and high-throughput chromosome conformation capture (Hi-C) sequencing, HIVID HPV-capture sequencing, RNA sequencing, and whole-genome bisulfite sequencing High-throughput HPV capture sequencing, whole-exome sequencing, transcriptome sequencing, proteomics, phosphoproteomics, and single-cell RNA sequencing Hi-C sequencing, whole-genome sequencing, RNA sequencing, Ch
Technology Multi-omics Second-generation sequencing Second-generation sequencing Second-generation sequencing Second-generation sequencing
Table 1. (Continued) Cancer type Small cell cervical carcinoma Endocervical adenocarcinomas Mucoepidermoid carcinomas Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 9 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.2034