Page 59 - GTM-3-2
P. 59
Global Translational Medicine Hesperetin alleviates pulmonary injury
A B C
D E F
G H
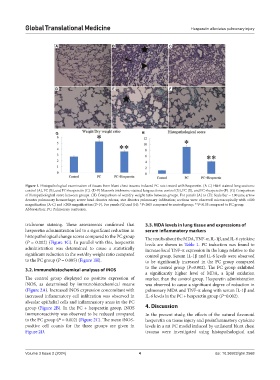
Figure 1. Histopathological examination of tissues from blunt chest trauma-induced PC rats treated with hesperetin. (A-C) H&E-stained lung sections:
control (A), PC (B), and PC+hesperetin (C). (D-F) Masson’s trichrome-stained lung sections: control (D), PC (E), and PC+hesperetin (F). (G) Comparison
of histopathological score between groups. (H) Comparison of wet/dry weight ratio between groups. For panels (A) to (F): Scale bar = 100 µm; arrow
denotes pulmonary hemorrhage; arrow head denotes edema; star denotes pulmonary infiltration; sections were observed microscopically with ×100
magnification (A-C) and ×200 magnification (D-F). For panels (G) and (H): *P<0.05 compared to control group; **P<0.05 compared to PC group.
Abbreviation: PC: Pulmonary contusion.
trichrome staining. These assessments confirmed that 3.3. MDA levels in lung tissue and expressions of
hesperetin administration led to a significant reduction in serum inflammatory markers
histopathological change scores compared to the PC group The results about the MDA, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 cytokine
(P = 0.002) (Figure 1G). In parallel with this, hesperetin levels are shown in Table 1. PC induction was found to
administration was determined to cause a statistically increase local TNF-α expression in the lungs relative to the
significant reduction in the wet/dry weight ratio compared control group. Serum IL-1β and IL-6 levels were observed
to the PC group (P = 0.005) (Figure 1H). to be significantly increased in the PC group compared
3.2. Immunohistochemical analyses of iNOS to the control group (P=0.002). The PC group exhibited
a significantly higher level of MDA, a lipid oxidation
The control group displayed no positive expression of marker, than the control group. Hesperetin administration
iNOS, as determined by immunohistochemical means was observed to cause a significant degree of reduction in
(Figure 2A). Increased iNOS expression concomitant with pulmonary MDA and TNF-α along with serum IL-1β and
increased inflammatory cell infiltration was observed in IL-6 levels in the PC + hesperetin group (P=0.002).
alveolar epithelial cells and inflammatory areas in the PC
group (Figure 2B). In the PC + hesperetin group, iNOS 4. Discussion
immunoreactivity was observed to be reduced compared In the present study, the effects of the natural flavonoid
to the PC group (P = 0.002) (Figure 2C). The mean iNOS- hesperetin on tissue injury and proinflammatory cytokine
positive cell counts for the three groups are given in levels in a rat PC model induced by unilateral blunt chest
Figure 2D. trauma were investigated using histopathological and
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/gtm.2568