Page 60 - GTM-3-2
P. 60
Global Translational Medicine Hesperetin alleviates pulmonary injury
A B orange, has a variety of pharmacological functions, such
as antioxidative, antiapoptotic, and anti-inflammatory
effects. Recent research has reported that hesperetin has
19
protective/therapeutic effects on disease models featuring
progressive inflammation, especially those of ulcerative
colitis, osteoarthritis, acute pulmonary injury, neuronal
degeneration, and liver injury. 20-23
C D Trauma is the most common cause of death in the first
20 years of life and represents one of the most common
causes of fatality after cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
3
Blunt chest trauma damages tissue integrity and may injure
tissues and organs in the chest cavity. Vehicular accidents,
work accidents, and falls from heights are some examples of
the situations where multiple traumas are observed along
24
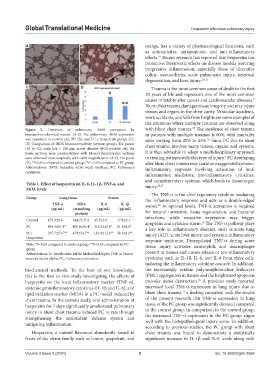
Figure 2. Detection of pulmonary iNOS expression by with blunt chest trauma. The incidence of chest trauma
immunohistochemical means. (A-C) The pulmonary iNOS expression in patients with multiple traumas is 60%, with mortality
was examined in control (A), PC (B), and PC + hesperetin groups (C). rates varying from 20% to 25%. Since PC due to blunt
25
(D) Comparison of iNOS immunoreactivity between groups. For panels chest trauma involves many tissues, organs, and systems,
(A) to (C): scale bar = 100 µm; arrow denotes iNOS-positive cell; the
tissue sections were counterstained with Mayer’s hematoxylin; sections it is thus advisable to adopt a multidisciplinary approach
3
were observed microscopically with ×400 magnification (A-C). For panel to treating patients with this type of injury. PC developing
(D): *P<0.05 compared to control group; **P < 0.05 compared to PC group. after blunt chest trauma may cause an exaggerated systemic
Abbreviations: iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; PC: Pulmonary inflammatory response involving activation of local
contusion.
inflammation mediators, pro-inflammatory cytokines,
and complementary systems, which leads to tissue/organ
Table 1. Effect of hesperetin on IL-6, IL-1 β, TNF-α, and 26,27
MDA levels injury.
The TNF-α is the chief regulatory cytokine mediating
Group Lung tissue Serum the inflammatory response and acts as a double-edged
TNF-α MDA IL-6 IL-1β sword. At optimal levels, TNF-α activation is required
28
(pg/mL) (mmol/mg (pg/mL) (pg/mL)
protein) for natural immunity, tissue regeneration, and bacterial
Control 175.3±9.6 544.7±37.2 45.5±3.9 17.8±3.1 infections, while excessive expression may trigger
apoptosis and cytokine storm. The TNF-α pathway plays
29
PC 454.3±51.8* 400.8±50.4* 316.2±13.8* 61.9±8.6* a key role in inflammatory diseases, such as acute lung
PC+ 297.7±53.7** 479±24.7** 181.8±12.4** 38.3±4.2** injury (ALI), acute liver injury, and systemic inflammatory
Hesperetin response syndrome. Dysregulated TNF-α during acute
Note: *P<0.05 compared to control group. **P<0.05 compared to PC tissue injury activates neutrophils and macrophages
group.
Abbreviations: IL: Interleukin; MDA: Malondialdehyde; TNF-α: Tumor present in tissues and causes release of pro-inflammatory
necrosis factor-alpha; PC: Pulmonary contusion. cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 from these cells,
inducing the inflammatory cytokine cascade. In addition,
biochemical methods. To the best of our knowledge, the increasingly evident polymorphonuclear leukocyte
this is the first in vivo study investigating the effects of (PML) aggregation in tissues and the heightened apoptosis
30
hesperetin on the local inflammatory marker (TNF-α), provoke tissue destruction. A previous study reported
systemic proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β and IL-6), and increased local TNF-α expression in lung injury due to
31
lipid oxidation marker (MDA) in a PC model induced by blunt chest trauma, a finding consistent with the results
chest trauma. In the current study, oral administration of of the present research that TNF-α expression in lung
hesperetin for 7 days significantly ameliorated pulmonary tissue of the PC group was significantly elevated compared
injury in blunt chest trauma-induced PC in rats through to the control group. In comparison to the control group,
strengthening the antioxidant defense system and the increased TNF-α expression in the PC group aligns
mitigating inflammation. well with the histopathological injury score. In addition,
according to previous studies, the PC group with blunt
Hesperetin, a natural flavonoid abundantly found in chest trauma was found to demonstrate a statistically
fruits of the citrus family such as lemon, grapefruit, and significant increase in IL-1β and IL-6 levels along with
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/gtm.2568