Page 98 - GTM-3-2
P. 98
Global Translational Medicine Targeted detection in Barrett’s neoplasia
linker was used to optimize the separation between the and delivered fluorescence and reflectance signals to
individual peptides to match the mean distance between detectors of a portable cart that is transported into the
these targets expressed on the mucosal surface. The procedure room 12,13 (Figure 3B and C).
fluorophore was chosen to have minimal spectral overlap
with the WL illumination from a conventional endoscope 2.3.3. Image analysis
(Figure 2B). Specific binding by the peptide heterodimer to Reflectance and fluorescence signals were mapped onto
EGFR and HER2 in Barrett’s neoplasia was validated with the blue and green channels. A custom Chan–Vese
tissue staining of human specimens ex vivo. The NIR- algorithm was used to segment the target from the region
16
14
labeled peptide heterodimer was synthesized as per the of interest (ROI) within video frames. The region around
current good manufacturing practices and was lyophilized the target (30-pixel-wide) was considered the background
and aliquoted (1.8 mg) in 10 mL amber vials to protect region. The target-to-background (T/B) ratio calculation
them from light. The purity of the peptide heterodimer was performed by comparing the mean intensity of the
was determined as ≥95.0% by high-performance liquid target (T) and background (B) regions. The T/B ratios were
chromatography, and its stability was assessed based on used to classify the ROI as either positive (HGD/EAC) or
visual appearance, purity, and molecular weight. negative (LGD/BE/squamous epithelium).
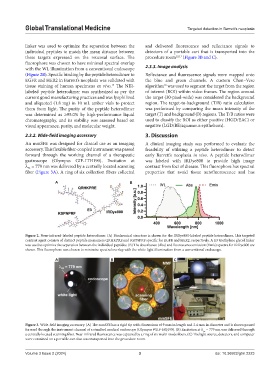
2.3.2. Wide-field imaging accessory 3. Discussion
An mmSFE was designed for clinical use as an imaging A clinical imaging study was performed to evaluate the
accessory. This flexible fiber-coupled instrument was passed feasibility of utilizing a peptide heterodimer to detect
forward through the working channel of a therapeutic early Barrett’s neoplasia in vivo. A peptide heterodimer
gastroscope (Olympus GIF-1TH190). Excitation at was labeled with IRDye800 to provide high image
λ ex = 779 nm was delivered by a centrally located scanning contrast from foci of disease. This fluorophore has spectral
fiber (Figure 3A). A ring of six collection fibers collected properties that avoid tissue autofluorescence and has
A B
Figure 2. Near-infrared-labeled peptide heterodimer. (A) Biochemical structure is shown for the IRDye800-labeled peptide heterodimer. This targeted
contrast agent consists of distinct peptide monomers QRHKPRE and KSPNPRF specific for EGFR and HER2, respectively. A E3 triethylene glycol linker
was used to optimize the separation between the individual peptides. (B) The absorbance (Abs) and fluorescence emission (Emis) spectra for IRDye800 are
shown. This fluorophore was chosen to minimize spectral overlap with the white light illumination from a conventional endoscope.
A B C
Figure 3. Wide-field imaging accessory. (A) The mmSFE has a rigid tip with dimensions of 9 mm in length and 2.4 mm in diameter and is shown passed
forward through the instrument channel of a standard medical endoscope (Olympus #GIF-HQ190). (B) Excitation at λ = 779 nm was delivered through
ex
a centrally located scanning fiber. Near-infrared fluorescence was captured by a ring of six multi-mode fibers. (C) The light source, detectors, and computer
were contained on a portable cart that was transported into the procedure room.
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 3 doi: 10.36922/gtm.2223