Page 45 - GTM-3-3
P. 45
Global Translational Medicine Ocular changes in Alzheimer’s disease
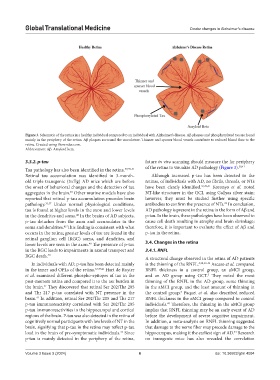
Figure 3. Schematic of the retina in a healthy individual compared to an individual with Alzheimer’s disease. Aβ plaques and phosphorylated tau are found
mainly in the periphery of the retina. Aβ plaques surround the vasculature. Thinner and sparser blood vessels contribute to reduced blood flow to the
retina. Created using Biorender.com.
Abbreviation: Aβ: Amyloid beta.
3.3.2. p-tau future in vivo scanning should measure the far periphery
Tau pathology has also been identified in the retina. 37,39-41 of the retina to visualize AD pathology (Figure 3). 39,41
Retinal tau accumulation was identified in 3-month- Although increased p-tau has been detected in the
old triple transgenic (3×Tg) AD mice which are before retinas, of individuals with AD, no fibrils, threads, or NTs
the onset of behavioral changes and the detection of tau have been clearly identified. 37,39,41 Koronyo et al. noted
aggregates in the brain. Other murine models have also NT-like structures in the GCL using Gallyas silver stain;
40
reported that retinal p-tau accumulation precedes brain however, they must be studied further using specific
22
pathology. 31,37 Under normal physiological conditions, antibodies to confirm the presence of NTs. In conclusion,
tau is found at higher levels in the axon and lower levels AD pathology is present in the retina in the form of Aβ and
in the dendrites and soma. In the brains of AD subjects, p-tau. In the brain, these pathologies have been observed to
42
p-tau detaches from the axon and accumulates in the cause cell death resulting in atrophy and brain shrinkage;
soma and dendrites. This finding is consistent with what therefore, it is important to evaluate the effect of Aβ and
42
occurs in the retina; greater levels of tau are found in the p-tau in the retina.
retinal ganglion cell (RGC) soma, and dendrites, and
lower levels are seen in the axon. The presence of p-tau 3.4. Changes in the retina
40
in the RGC leads to impairments in axonal transport and 3.4.1. RNFL
RGC death. 40
A structural change observed in the retina of AD patients
In individuals with AD, p-tau has been detected mainly is the thinning of the RNFL. 5,30,43-46 Ascaso et al. compared
in the inner and OPLs of the retina. 37,39,41 Hart de Ruyter RNFL thickness in a control group, an aMCI group,
et al. examined different phospho-epitopes of tau in the and an AD group using OCT. They noted the most
5
post-mortem retina and compared it to the tau burden in thinning of the RNFL in the AD group, some thinning
the brain. They discovered that retinal Ser 202/Thr 205 in the aMCI group, and the least amount of thinning in
41
and Thr 217 p-tau correlated with NT presence in the the control group. Paquet et al. also described reduced
5
brain. In addition, retinal Ser 202/Thr 205 and Thr 217 RNFL thickness in the aMCI group compared to control
41
p-tau immunoreactivity correlated with Ser 202/Thr 205 individuals. Therefore, the thinning in the aMCI group
43
p-tau immunoreactivities in the hippocampal and cortical implies that RNFL thinning may be an early event of AD
regions of the brain. P-tau was also detected in the retina of before the development of severe cognitive impairment.
cognitively normal participants with low levels of NT in the In addition, a meta-analysis on RNFL thinning suggested
brain, signifying that p-tau in the retina may reflect p-tau that damage to the nerve fiber may precede damage to the
load in the brain of pre-symptomatic individuals. Since hippocampus, making it the earliest sign of AD. Research
41
44
p-tau is mainly detected in the periphery of the retina, on transgenic mice has also revealed the correlation
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2024) 6 doi: 10.36922/gtm.4094