Page 41 - GTM-3-3
P. 41
Global Translational Medicine Ocular changes in Alzheimer’s disease
86,000 new cases of dementia are diagnosed in Canada foreign material and initiate an inflammatory response
yearly, and of the nearly 477,000 seniors in Canada living involving microglia and astrocytes which produce
8
with dementia, 2/3 are women. Globally, women have a cytokines and free radicals that will eventually cause
9
1.17 times higher prevalence of AD compared to men. cell death and neurodegeneration. Aβ aggregates also
10
1
Along with the increased prevalence of AD comes the bind to redox-active metals to produce reactive oxygen
increased economic and social burden of caring for the species (ROS), leading to mitochondrial damage and
AD population. 7 neuronal toxicity. Furthermore, Aβ42 triggers the
1
hyperphosphorylation of the microtubule-binding protein
2.2. Pathology tau. Hyperphosphorylation causes tau to dissociate from
12
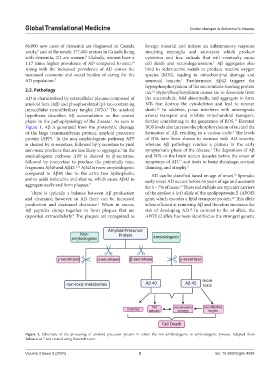
AD is characterized by extracellular plaques composed of the microtubule, fold abnormally, and aggregate to form
amyloid beta (Aβ) and phosphorylated (p)-tau-containing NTs that destroy the cytoskeleton and lead to neuron
3
intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (NTs). The amyloid death. In addition, p-tau interferes with anterograde
12
hypothesis describes Aβ accumulation as the central axonal transport and inhibits mitochondrial transport,
player in the pathophysiology of the disease. As seen in further contributing to the generation of ROS. Elevated
1
11
Figure 1, Aβ is generated from the proteolytic cleavage ROS levels also increase the phosphorylation of tau and the
1
of the large transmembrane protein, amyloid precursor formation of Aβ, resulting in a vicious cycle. The levels
protein (APP). In the non-amyloidogenic pathway, APP of NTs have been shown to increase with AD severity,
1
is cleaved by α-secretase, followed by γ-secretase to yield whereas Aβ pathology reaches a plateau in the early
non-toxic products that are less likely to aggregate. In the symptomatic phase of the disease. The deposition of Aβ
3
1
amyloidogenic pathway APP is cleaved by β-secretase, and NTs in the brain occurs decades before the onset of
followed by γ-secretase to produce the potentially toxic symptoms of AD, and leads to brain shrinkage, cortical
13
fragments Aβ40 and Aβ42. Aβ42 is more amyloidogenic thinning, and atrophy. 3
3,11
compared to Aβ40 due to the extra two hydrophobic AD can be classified based on age of onset. Sporadic
12
amino acids isoleucine and alanine, which cause Aβ42 to early-onset AD occurs before 65 years of age and accounts
aggregate easily and form plaques. 3 for 3 – 7% of cases. These individuals are typically carriers
12
There is typically a balance between Aβ production of the epsilon 4 (ε4) allele of the apolipoprotein E (APOE)
and clearance; however, in AD there can be increased gene, which encodes a lipid transport protein. This allele
12
production and decreased clearance. When in excess, is less efficient at removing Aβ and therefore increases the
1
Aβ peptides clump together to form plaques that are risk of developing AD. In contrast to the ε4 allele, the
12
deposited extracellularly. The plaques are recognized as APOE ε2 allele has been identified as the strongest genetic
3
Figure 1. Schematic of the processing of amyloid precursor protein in either the non-amyloidogenic or amyloidogenic process. Adapted from
Sultan et al. and created using Biorender.com.
12
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2024) 2 doi: 10.36922/gtm.4094