Page 72 - GTM-3-4
P. 72
Global Translational Medicine New neck examination for sleep apnea
on self-reported symptoms such as snoring and daytime
sleepiness but do not assess the abnormal physiology that
treatments such as CPAP are designed to correct.
An important but unanswered question is, “which site
of airway obstruction is identified by the DGT?” Although
the DGT is initiated at the tongue base/hyoid area, we do
not as yet have manometry data to indicate exactly which
levels of the airway are affected by the DGT. Given the
superior-posterior direction of its force vector, the DGT
could possibly be affecting higher levels of the airway.
However, there have been several experimental and review
papers that have identified the sites of obstruction in
various OSA patients.
Katsantonis et al. studied 20 OSA patients during
27
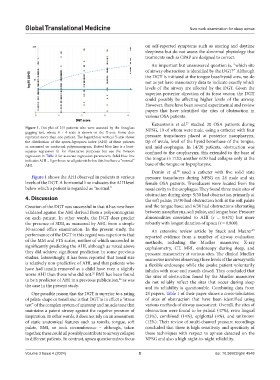
Figure 1. Dot plot of 215 patients who were assessed by the Douglass NPSG, 19 of whom were male, using a catheter with four
gagging test, whose 0 – 4 scale is shown on the X-axis. Some dots
represent more than one patient. The logarithmic vertical Y-axis shows pressure transducers placed at posterior nasopharynx,
the distribution of the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) of these patients tip of uvula, level of the hyoid bone/base of the tongue,
as measured on nocturnal polysomnogram. Dotted blue line is a least- and mid-esophagus. In 14/20 patients, obstruction was
squares regression fit for illustrative purposes but see the Poisson confined to the oropharynx; this extended to the base of
regression in Table 2 for accurate regression parameters. Solid blue line the tongue in 7/20; another 6/20 had collapse only at the
indicates AHI = 5 per hour, so all patients below this line have a “normal”
AHI. base of the tongue or hypopharynx.
Demin et al. used a catheter with five solid state
28
Figure 1 shows the AHI observed in patients at various pressure transducers during NPSG on 24 male and six
levels of the DGT. A horizontal line indicates the AHI level female OSA patients. Transducers were located from the
below which a patient is regarded as “normal.” nasal cavity to the esophagus. They found three main sites of
obstruction during sleep: 9/30 had obstruction primarily at
4. Discussion the soft palate; 15/30 had obstruction both at the soft palate
Creation of the DGT was successful in that it has now been and the tongue base; and 6/30 had obstructions alternating
validated against the AHI derived from a polysomnogram between nasopharynx, soft palate, and tongue base. Pressure
on each patient. In other words, the DGT does predict abnormalities correlated to AHI (r = 0.471) but more
the presence of SDB, as measured by AHI, from a simple robustly with longest duration of apnea (r = 0.800).
30-second office examination. In the present study, the An extensive review article by Stuck and Maurer
29
performance of the DGT in this regard was superior to that reported evidence from a number of airway evaluation
of the MM and FTS scales, neither of which succeeded in methods, including the Mueller maneuver, X-ray
significantly predicting the AHI, although as noted above cephalometry, CT, MRI, endoscopy during sleep, and
they did achieve significant prediction in some previous pressure manometry at various sites. The clinical Mueller
studies. Interestingly, it has been reported that tonsil size maneuver involves observing three levels of the airway with
is relatively non-predictive of AHI, and that patients who a flexible endoscope while the awake patient voluntarily
have had tonsils removed as a child have even a slightly inhales with nose and mouth closed. They concluded that
worse AHI than those who did not. BMI has been found the sites of obstruction found by the Mueller maneuver
25
to be a predictor of AHI in a previous publication, as was do not reliably reflect the sites that occur during sleep
26
the case in the present study. and its reliability is questionable. Combining data from
One possible reason that the DGT is superior to a rating 23 papers, Table 1 of their paper shows a cross-tabulation
of palate shape or tonsil size is that DGT is in effect a “stress of sites of obstruction that have been identified using
test” of the complex system of anatomy and muscle tone that various methods of airway assessment. Overall, the sites of
maintains a patent airway against the negative pressure of obstruction were found to be palatal (47%), retro lingual
inspiration. In other words, it does not rely on an assessment (23%), combined (14%), epiglottal (4%), and unknown
of static anatomical features such as tonsils, tongue, soft (12%). Their review of multi-channel pressure recordings
palate, BMI, or neck circumference – although, taken concluded that there is high sensitivity and specificity of
together, these could all possibly contribute to airway collapse these techniques with respect to apneas detected on the
in different patients. In contrast, apnea questionnaires focus NPSG and also a high night-to-night reliability.
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/gtm.4548