Page 113 - GTM-4-2
P. 113
Global Translational Medicine Platelet aggregation inhibition by 2-isoxazolines
layer chromatography on Silufol UV-254 plates (Merck, ddd, J = 8.1, 7.7, 0.5 Hz), and 7.65 (1H, ddd, J = 7.7,
Germany). 1.7, 1.2 Hz). The C NMR shows δ 41.8 (1C, s),
13
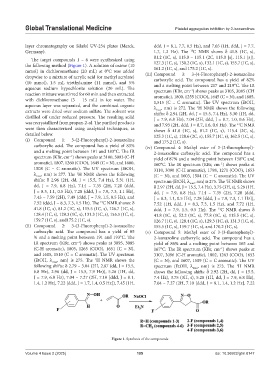
The target compounds 1 – 6 were synthesized using 81.2 (1C, s), 115.0 – 115.1 (2C, 115.0 [s], 115.1 [s]),
the following method (Figure 1). A solution of oxime (10 127.3 (1C, s), 130.2 (1C, s), 132.1 (1C, s), 155.7 (1C, s),
mmol) in dichloromethane (20 mL) at 0°C was added 161.2 (1C, s), and 175.2 (1C, s).
dropwise to a mixture of acrylic acid (or methyl acrylate) (iii) Compound 3: 3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-2-isoxazoline
carboxylic acid. The compound has a yield of 82%
(10 mmol), 1.5 mL triethylamine (11 mmol), and 5% and a melting point between 217 and 219°С. The IR
aqueous sodium hypochlorite solution (20 mL). The spectrum (KBr, cm ) shows peaks as 3105, 3085 (CH
−1
reaction mixture was stirred for 60 min and then extracted aromatic), 1800, 1255 (COO), 1645 (C = N), and 1605,
with dichloromethane (3 – 15 mL) in ice water. The 1,515 (C = C aromatic). The UV spectrum (EtOH,
aqueous layer was separated, and the combined organic λ , nm) is 272. The H NMR shows the following
1
max
extracts were dried over sodium sulfate. The solvent was shifts: δ 2.94 (2H, dd, J = 15.5, 7.4 Hz), 5.30 (1H, dd,
distilled off under reduced pressure. The resulting solid J = 7.9, 6.8 Hz), 7.04 (2H, ddd, J = 8.7, 1.0, 0.6 Hz),
was recrystallized from propan-2-ol. The purified products and 7.93 (2H, ddd, J = 8.7, 1.6, 0.6 Hz). The C NMR
13
were then characterized using analytical techniques, as shows δ 41.8 (1C, s), 81.2 (1C, s), 115.4 (2C, s),
detailed below. 125.3 (1C, s), 128.6 (2C, s), 155.7 (1C, s), 162.5 (1C, s),
(i) Compound 1: 3-(2-Fluorophenyl)-2-isoxazoline and 175.2 (1C, s).
carboxylic acid. The compound has a yield of 83% (iv) Compound 4: Methyl ester of 3-(2-fluorophenyl)-
and a melting point between 181 and 183°С. The IR 2-isoxazoline carboxylic acid. The compound has a
spectrum (KBr, cm ) shows peaks at 3100, 3093 (C-H yield of 87% and a melting point between 158°С and
−1
aromatic), 1807, 1260 (COO), 1649 (C = N), and 1600, 160°С. The IR spectrum (KBr, cm ) shows peaks at
−1
1508 (C = C aromatic). The UV spectrum (EtOH, 3110, 3090 (C-H aromatic), 1798, 1271 (COO), 1653
λ max , nm) is 277. The H NMR shows the following (C = N), and 1603, 1504 (C = C aromatic). The UV
1
shifts: δ 2.96 (2H, dd, J = 15.5, 7.4 Hz), 5.31 (1H, spectrum (EtOH, λ , nm) is 275. The H NMR shows
1
max
dd, J = 7.9, 6.8 Hz), 7.14 – 7.35 (2H, 7.20 (ddd, δ 2.97 (2H, dd, J = 15.5, 7.4 Hz), 3.75 (3H, s), 5.29 (1H,
J = 8.3, 1.1, 0.5 Hz), 7.28 (ddd, J = 7.9, 7.3, 1.1 Hz), dd, J = 7.9, 6.8 Hz), 7.14 – 7.35 (2H, 7.20 [ddd,
7.43 – 7.59 (2H), 7.49 (ddd, J = 7.9, 1.5, 0.5 Hz), and J = 8.3, 1.1, 0.5 Hz], 7.28 [ddd, J = 7.9, 7.3, 1.1 Hz]),
13
7.52 (ddd, J = 8.3, 7.3, 1.5 Hz). The C NMR shows: δ 7.52 (1H, ddd, J = 8.3, 7.3, 1.5 Hz), and 7.72 (1H,
41.8 (1C, s), 81.2 (1C, s), 115.5 (1C, s), 126.7 (1C, s), ddd, J = 7.9, 1.5, 0.5 Hz). The C NMR shows δ
13
128.4 (1C, s), 129.3 (1C, s), 131.3 (1C, s), 155.5 (1C, s), 41.8 (1C, s), 52.2 (1C, s), 77.8 (1C, s), 115.5 (1C, s),
159.7 (1C, s), and175.2 (1C, s). 126.7 (1C, s), 128.4 (1C, s), 129.3 (1C, s), 131.3 (1C, s),
(ii) Compound 2: 3-(3-Fluorophenyl)-2-isoxazoline 155.5 (1C, s), 159.7 (1C, s), and 170.2 (1C, s).
carboxylic acid. The compound has a yield of 85 (v) Compound 5: Methyl ester of 3-(3-fluorophenyl)-
% and a melting point between 191 and 193°С. The 2-isoxazoline carboxylic acid. The compound has a
IR spectrum (KBr, cm ) shows peaks at 3095, 3085 yield of 86% and a melting point between 165 and
−1
(C-H aromatic), 1805, 1265 (COO), 1651 (C = N), 167°С. The IR spectrum (KBr, cm ) shows peaks at
−1
and 1605, 1510 (C = C aromatic). The UV spectrum 3107, 3096 (C-H aromatic), 1802, 1263 (COO), 1653
(EtOH, λ max , nm) is 275. The H NMR shows the (C = N), and 1607, 1509 (C = C aromatic). The UV
1
following shifts: δ 2.79 – 3.04 (2H, 2.87 (dd, J = 15.5, spectrum (EtOH, λ max , nm) is 273. The H NMR
1
6.8 Hz), 2.96 (dd, J = 15.5, 7.9 Hz)), 5.26 (1H, dd, shows the following shifts: δ 2.92 (2H, dd, J = 15.5,
J = 7.9, 6.8 Hz), 7.04 – 7.27 (2H, 7.10 [ddd, J = 8.1, 7.4 Hz), 3.75 (3H, s), 5.28 (1H, dd, J = 7.9, 6.8 Hz),
1.4, 1.2 Hz], 7.22 [ddd, J = 1.7, 1.4, 0.5 Hz]), 7.45 (1H, 7.04 – 7.27 (2H, 7.10 [ddd, J = 8.1, 1.4, 1.2 Hz], 7.22
Figure 1. Synthesis of the compounds
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 105 doi: 10.36922/gtm.8147