Page 38 - GTM-4-3
P. 38
Global Translational Medicine Electrical stimulation in therapy and biology
as enhanced wound healing and tissue regeneration, are electrical circuit malfunctions, and signal variability, all of
59
well-documented and supported by several studies, the which could cause adverse effects or therapeutic failure in
61
long-term impacts of prolonged ES application remain clinical applications. The examined device-related issues
ambiguous. According to some researchers, electrical fields further complicate the use of ES in clinical practice since
may deteriorate cells, alter gene function, or contribute to standard tools utilized for the interventions are sufficiently
carcinogenic changes in some instances. In addition, the safe and comparable across studies (Table 2).
60
systematic effects of ES on neighboring organs and tissues, These three problems, the variability of cellular
particularly in in vivo models, have not been thoroughly response, the absence of optimized stimulation parameters,
explored. The lack of information on the procedure’s long- and the uncertain side effects of ES, prove that ES is not a
term effects on tissues and cells presents a significant simple therapeutic approach. However, the field is still in
challenge to its safe implementation, especially in strategies its early stages. Further research is necessary to standardize
that involve continuous stimulation over months or years, the protocols for applying ES, optimize the parameters,
for chronic diseases or tissue regeneration. Safety concerns and understand the long-term effects of ES on cells and
are further heightened by device failure, heat generation, tissues. Addressing these challenges will be essential for
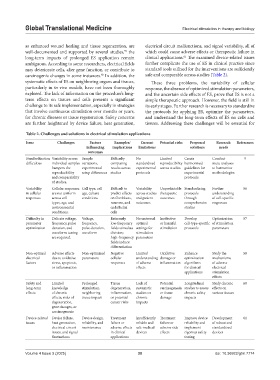
Table 2. Challenges and solutions in electrical stimulation applications
Issue Challenges Factors Examples/ Current Potential risks Proposed Research References
influencing implications limitations solutions needs
outcomes
Standardization Variability across Sample Difficulty No Limited Create Conduct 9
difficulties individual samples variations, comparing standardized reproducibility harmonized meta-analyses
hampers the experimental results across experimental across studies guidelines for to harmonize
reproducibility setup differences studies protocols experimental methodologies
and comparability protocols
of studies.
Variability Cellular responses Cell type, cell Difficult to Variability Unpredictable Standardizing Further 56
in cellular are not uniform age, culture predict effects across studies therapeutic protocols understanding
responses across cell conditions on fibroblasts, and patient outcomes through of cell-specific
types, age, and neurons, and outcomes comprehensive responses
environmental endothelial studies
conditions. cells
Difficulty in Delicate voltage, Voltage, Extremely No universal Ineffective Develop Optimization 57
parameter frequency, pulse frequency, low-frequency optimal or harmful cell-type-specific of stimulation
optimization duration, and pulse duration, fields stimulate settings for stimulation protocols parameters
waveform tuning waveform division; stimulation
are required. high-frequency parameters
fields induce
differentiation
Non-optimal Adverse effects Non-optimized Negative Limited Oxidative Enhance Study the 58
electrical due to oxidative parameters cellular understanding damage or optimization mechanisms
factors stress, apoptosis, responses of adverse inflammation algorithms of adverse
or inflammation effects for clinical electrical
applications stimulation
effects
Safety and Limited Prolonged Tissue Lack of Potential Longitudinal Study chronic 60
long-term knowledge stimulation, degeneration, systematic carcinogenesis studies to assess effects on
effects of chronic neighboring inflammation, studies on or tissue chronic safety various tissues
effects; risks of tissue impact or potential chronic damage impacts
degeneration, cancer risks impacts
gene changes, or
carcinogenesis
Device-related Device failure, Device design, Treatment Insufficiently Treatment Improve device Development 61
issues heat generation, reliability, and failure or reliable and failure or reliability and of robust and
electrical circuit maintenance adverse effects safe medical adverse side implement standardized
issues, and signal in clinical devices effects rigorous safety devices
fluctuations applications testing
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 30 doi: 10.36922/gtm.7774