Page 13 - IJB-10-1
P. 13
International Journal of Bioprinting Magnetic (Bio)inks for tissue engineering
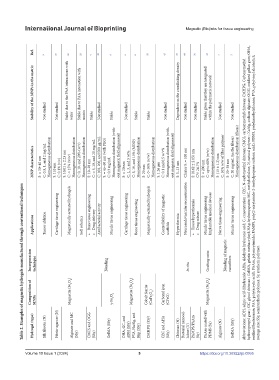
Ref. 9 27 22 23 4 58 6 3 8 95 45 35 89 34 46 7 5
Stability of the MNPs in the matrix Not studied Not studied Stable due to the PAA interactions with water Stable due to PAA interaction with matrix Stable Not studied Stable Not studied Stable Stable Not studied Dependent on the crosslinking density Not studied Not studied Stable given that they are integrated within the polymeric network Not studied Not studied
MNP characteristics S: ≈ 30–40 nm C: 0.5, 1, and 2 mg/mL Homogeneous distribution S: 110 nm C: 0.1% (v/v) S: 10.01 ± 2.23 nm C: ≈ 15% (w/w) Homogeneous distribution C: 0, 10, and 20% (w/v) Homogeneous distribution S: 10–20 nm C: ≈ 5, 10, and 20 mg/mL C: 100, 200, and 500 μg/mL S: ≈ 45–60 nm (with PEG) C: 0.3 mg/mL Homogeneous distribution (with- out magnetic field alignment) S: ≈ 20 nm C: 1, 3, and 5 wt% C: 5, 10, and 15% (MGO) Homogeneou
Table 2. Examples of magnetic hydrogels manufactured through conventional techniques
Applications Tumor ablation Cartilage tissue engineering Magnetically-actuated hydrogels Soft robotics Bone tissue engineering • Drug delivery • Antibacterial activity Muscle tissue engineering Cartilage tissue engineering Bone tissue engineering Magnetically-actuated hydrogels Controllability of magnetic scaffolds Hyperthermia Neuroendovascular reconstruction Tissue hyperthermia • Drug release • Muscle tissue engineering Implanta
Incorporation technique Blending In situ Grafting-onto Blending of magnetic nanofibers
Composition of MNPs Magnetite (Fe 3 O 4 ) γ-Fe 2 O 3 Magnetite (Fe 3 O 4 ) Cobalt ferrite (CoFe 2 O 4 ) Carbonyl iron (CFeO) Magnetite (Fe 3 O 4 ) average size; SSy, semisynthetic polymer; Sy, synthetic polymer.
Hydrogel (type) Silk fibroin (N) Fibrin-agarose (N) Alginate and MC (SSy) CMCS and OGG (SSy) GelMA (SSy) OHA, GC, and ADH (SSy) PVA, NaAlg, and Hap (SSy) CMHPG (SSy) CEC and AHA (SSy) Chitosan (N) Bacterial nanocel- lulose (N) PAMPS/PAAm (Sy) PAAm coated with PDMS (Sy) Alginate (N) GelMA (SSy)
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0965