Page 17 - IJB-10-1
P. 17
International Journal of Bioprinting Magnetic (Bio)inks for tissue engineering
Ref. 3 64 71 8 22 6 58 71 23
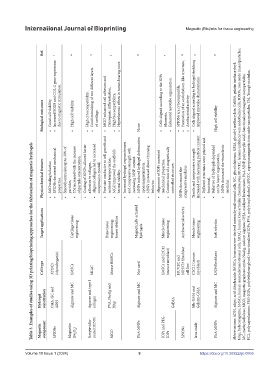
Increased SOX9 and COL-2 gene expression Good mimicking of two different layers MGO enhanced cell adhesion and Hyperthermic effects in tumor-bearing mice. Cells aligned according to the IOPs Enhanced myotube organization. Formation of an endothelium-like structure, Cells aligned according to hydrogel stretching improved myotube characteristics.
Biological outcomes Good cell viability, • • due to magnetic stimulation. High cell viability. • High cytocompatibility, • • of cartilage. • Osteogenic differentiation, High biocompatibility, • • None • filaments, • SPIONs are cytocompatible, • • Antibacterial activity. • • High cell viability
Table 3. Examples of studies using 3D printing/bioprinting approaches for the fabrication of magnetic hydrogels
Physicochemical features Self-healing behavior, • SPIONs decreased mechanical • properties. Smooth extrusion up to 30% of • particles, YM increased with the increase • of particle concentration. Coating of IONPs allowed better • adhesion to collagen, Aligned collagen led to increased • compression moduli. Pore size conducive to cell growth and • nutrient transportation, MGO improved the scaffold’s • hermal stability. Inc
Target applications Cartilage tissue engineering Bone tissue engineering; tumor ablation Magnetically-actuated hydrogels Muscle tissue engineering Antibacterial activity Muscle tissue engineering Soft robotics MC, methylcellulose; MGO, magnetic graphene oxide; NaAlg, sodium alginate; OHA, oxidized hyaluronate; PAA-MNP, poly(acrylic acid)-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles; PCL, polycaprolactone; PEG-IOPs, poly(ethylene glycol)-fun
Cell type ATDC5 (chondrogenic) hMSCs hKAC Mouse BMSCs Not used hMSCs and C2C12 (mouse myoblast) HUVEC and NIH3T3 fibroblast cell line C2C12 (mouse myoblast) L929 fibroblasts
Hydrogel constitution OHA, GC and ADH Alginate and MC Agarose and type I collagen PVA, NaAlg and HAp Alginate and MC GelMA Silk-GMA and Gelatin-GMA Alginate and MC
Magnetic component SPIONs Magnetite (Fe 3 O 4 ) Streptavidin- coated IONPs MGO PAA-MNPs IOPs and PEG- IOPs SPIONs Iron oxide PAA-MNPs
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 9 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0965