Page 14 - IJB-10-1
P. 14
International Journal of Bioprinting Magnetic (Bio)inks for tissue engineering
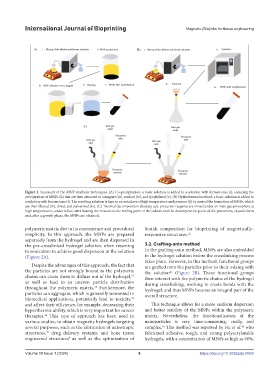
Figure 1. Summary of the MNP synthesis techniques. (A) Co-precipitation: a basic solution is added to a solution with ferrous ions (i), inducing the
precipitation of MNPs (ii) that are then attracted to a magnet (iii), washed (iv), and lyophilized (v). (B) Hydrothermal method: a basic solution is added to
a solution with ferrous ions (i). The resulting solution is kept in an autoclave at high temperature and pressure (ii) to control the formation of MNPs, which
are then filtered (iii), dried, and pulverized (iv). (C) Thermal decomposition (heating-up): precursor reagents are mixed under an inert gas atmosphere at
high temperatures, under reflux; after heating the mixture to the boiling point of the solvent and the decomposition point of the precursors, crystals form
and, after a growth phase, the MNPs are obtained.
polymeric matrix due to its convenience and procedural bioink composition for bioprinting of magnetically-
simplicity. In this approach, the MNPs are prepared responsive structures. 22
separately from the hydrogel and are then dispersed in
the pre-crosslinked hydrogel solution, often resorting 3.2. Grafting-onto method
to sonication to achieve good dispersion in the solution In the grafting-onto method, MNPs are also embedded
(Figure 2A). in the hydrogel solution before the crosslinking process
takes place. However, in this method, functional groups
Despite the advantages of this approach, the fact that are grafted onto the particles prior to their mixing with
the particles are not strongly bound to the polymeric the solution (Figure 2B). These functional groups
41
chains can cause them to diffuse out of the hydrogel, then interact with the polymeric chains of the hydrogel
42
as well as lead to an uneven particle distribution during crosslinking, working to create bonds with the
throughout the polymeric matrix. Furthermore, the hydrogel, and thus MNPs become an integral part of the
10
particles can aggregate, which is generally unwanted in overall structure.
biomedical applications, potentially lead to toxicity,
43
and affect their efficiency, for example, decreasing their This technique allows for a more uniform dispersion
hyperthermic ability, which is very important for cancer and better stability of the MNPs within the polymeric
therapies. This type of approach has been used in matrix. Nevertheless, the functionalization of the
44
various studies, to obtain magnetic hydrogels targeting nanoparticles is very time-consuming, costly, and
several purposes, such as the fabrication of anisotropic complex. This method was reported by Hu et al. who
41
46
structures, drug delivery systems, and bone tissue fabricated adhesive, tough, and strong polyacrylamide
45
engineered structures as well as the optimization of hydrogels, with a concentration of MNPs as high as 60%,
4
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0965