Page 174 - IJB-10-2
P. 174
International Journal of Bioprinting Coronavirus-infected bioprinted intestine
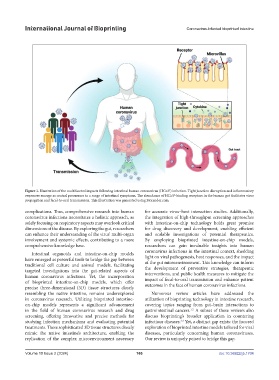
Figure 1. Illustration of the multifaceted impacts following intestinal human coronavirus (HCoV) infection. Tight junction disruption and inflammatory
responses emerge as central precursors to a range of intestinal symptoms. The abundance of HCoV-binding receptors in the human gut facilitates virus
propagation and fecal-to-oral transmission. This illustration was generated using Biorender.com.
complications. Thus, comprehensive research into human for accurate virus–host interaction studies. Additionally,
coronavirus infections necessitates a holistic approach, as the integration of high-throughput screening approaches
solely focusing on respiratory aspects may overlook critical with intestine-on-chip technology holds great promise
dimensions of the disease. By exploring the gut, researchers for drug discovery and development, enabling efficient
can enhance their understanding of the virus’ multi-organ and scalable investigations of potential therapeutics.
involvement and systemic effects, contributing to a more By employing bioprinted intestine-on-chip models,
comprehensive knowledge base. researchers can gain invaluable insights into human
coronavirus infections in the intestinal context, shedding
Intestinal organoids and intestine-on-chip models
have emerged as powerful tools to bridge the gap between light on viral pathogenesis, host responses, and the impact
of the gut microenvironment. This knowledge can inform
traditional cell culture and animal models, facilitating the development of preventive strategies, therapeutic
targeted investigations into the gut-related aspects of interventions, and public health measures to mitigate the
human coronavirus infections. Yet, the incorporation impact of fecal-to-oral transmission and enhance patient
of bioprinted intestine-on-chip models, which offer outcomes in the face of human coronavirus infections.
precise three-dimensional (3D) tissue structures closely
resembling the native intestine, remains underexplored Numerous review articles have addressed the
in coronavirus research. Utilizing bioprinted intestine- utilization of bioprinting technology in intestine research,
on-chip models represents a significant advancement covering topics ranging from gut–brain interactions to
in the field of human coronavirus research and drug gastrointestinal cancers. A subset of these reviews also
1,2
screening, offering innovative and precise methods for discuss bioprinting’s broader application in countering
studying infection mechanisms and evaluating potential infectious diseases. Yet, a distinct gap exists: the focused
3,4
treatments. These sophisticated 3D tissue structures closely exploration of bioprinted intestine models tailored for viral
mimic the native intestine’s architecture, enabling the diseases, particularly concerning human coronaviruses.
replication of the complex microenvironment necessary Our review is uniquely poised to bridge this gap.
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 166 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1704