Page 266 - IJB-10-2
P. 266
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting of boluses for radiotherapy
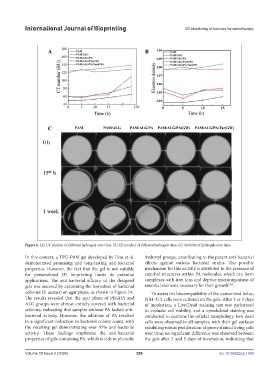
Figure 6. (A) CT number of different hydrogels over time. (B) ED number of different hydrogels time. (C) Stability of hydrogels over time.
In this context, a TPU-PAM gel developed by Hou et al. hydroxyl groups, contributing to the potent anti-bacterial
demonstrated promising and long-lasting anti-bacterial effects against various bacterial strains. The possible
properties. However, the fact that the gel is not suitable mechanism for this activity is attributed to the presence of
for personalized 3D bioprinting limits its potential catechol structures within PA molecules, which can form
applications. The anti-bacterial efficacy of the designed complexes with iron ions and deprive microorganisms of
[33]
gels was assessed by examining the formation of bacterial essential elements necessary for their growth .
colonies (S. aureus) on agar plates, as shown in Figure 5A. To assess the biocompatibility of the customized bolus,
The results revealed that the agar plates of PEGDA and NIH-3T3 cells were cultured on the gels. After 3 or 5 days
ALG groups were almost entirely covered with bacterial of incubation, a Live/Dead staining test was performed
colonies, indicating that samples without PA lacked anti- to evaluate cell viability, and a cytoskeletal staining was
bacterial activity. However, the addition of PA resulted conducted to examine the cellular morphology. Few dead
in a significant reduction in bacterial colony count, with cells were observed in all samples, with their gel surfaces
the resulting gel demonstrating over 95% anti-bacterial exhibiting robust proliferation of green-stained living cells
activity. These findings emphasize the anti-bacterial over time; no significant difference was observed between
properties of gels containing PA, which is rich in phenolic the gels after 3 and 5 days of incubation, indicating that
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 258 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1589