Page 350 - IJB-10-2
P. 350
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printing with drug for vascular repair
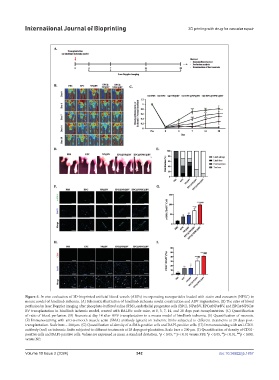
Figure 5. In vivo evaluation of 3D-bioprinted artificial blood vessels (ABVs) incorporating nanoparticles loaded with statin and curcumin (NPSC) in
mouse model of hindlimb ischemia. (A) Schematic illustration of hindlimb ischemia model construction and ABV implantation. (B) The ratio of blood
perfusion by laser Doppler imaging after phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), endothelial progenitor cells (EPC), NP@BV, EPC@NP@BV, and EPC@NPSC@
BV transplantation in hindlimb ischemic model, created with BALB/c nude mice, at 0, 3, 7, 14, and 28 days post-transplantation. (C) Quantification
of ratio of blood perfusion. (D) Necrosis at day 14 after ABV transplantation in a mouse model of hindlimb ischemia. (E) Quantification of necrosis.
(F) Immunostaining with anti-α-smooth muscle actin (SMA) antibody (green) on ischemic limbs subjected to different treatments at 28 days post-
transplantation. Scale bars = 200 µm. (G) Quantification of density of α-SMA-positive cells and DAPI-positive cells. (H) Immunostaining with anti-CD31
antibody (red) on ischemic limbs subjected to different treatments at 28 days post-plantation. Scale bars = 200 µm. (I) Quantification of density of CD31-
positive cells and DAPI-positive cells. Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 versus PBS. p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.001
#
###
##
versus NP.
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 342 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1857