Page 90 - IJB-10-2
P. 90
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed nanocomposites: Synthesis & applications
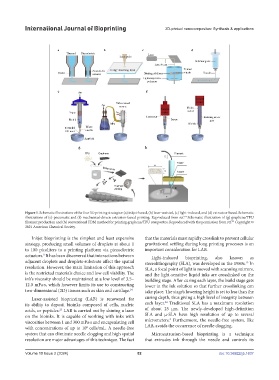
Figure 1. Schematic illustrations of the four 3D printing strategies: (a) inkjet-based, (b) laser-assisted, (c) light-induced, and (d) extrusion-based.Schematic
14
illustrations of (e) pneumatic and (f) mechanical-driven extrusion-based printing. Reproduced from ref. Schematic illustration of (g) graphene/TPU
filament production and (h) conventional FDM method for printing graphene/TPU composites. Reproduced with the permission from ref. Copyright ©
22
2021 American Chemical Society.
Inkjet bioprinting is the simplest and least expensive that the materials must rapidly crosslink to prevent cellular
strategy, producing small volumes of droplets at about 1 gravitational settling during long printing processes is an
to 100 picoliters to a printing platform via piezoelectric important consideration for LAB.
8
actuators. It has been discovered that interactions between Light-induced bioprinting, also known as
adjacent droplets and droplets-substrate affect the spatial stereolithography (SLA), was developed in the 1980s. In
19
resolution. However, the main limitation of this approach SLA, a focal point of light is moved with scanning mirrors,
is the restricted materials choice and low cell viability. The and the light-sensitive liquid inks are crosslinked on the
ink’s viscosity should be maintained at a low level of 3.5– building stage. After curing each layer, the build stage gets
12.0 mPa·s, which however limits its use to constructing lower in the ink solution so that further crosslinking can
two-dimensional (2D) tissues such as skin and cartilage. 14 take place. The stage’s lowering height is set to less than the
Laser-assisted bioprinting (LAB) is renowned for curing depth, thus giving a high level of integrity between
24
its ability to deposit bioinks composed of cells, nucleic each layer. Traditional SLA has a maximum resolution
acids, or peptides. LAB is carried out by shining a laser of about 25 μm. The newly-developed high-definition
23
on the bioinks. It is capable of working with inks with SLA and μ-SLA have high resolution of up to several
8
viscosities between 1 and 300 mPa·s and encapsulating cell micrometers. Furthermore, the needle-free system, like
with concentrations of up to 10 cells/mL. A needle-free LAB, avoids the occurrence of needle clogging.
8
system that can eliminate needle clogging and high spatial Microextrusion-based bioprinting is a technique
resolution are major advantages of this technique. The fact that extrudes ink through the needle and controls its
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 82 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1637