Page 14 - IJB-3-2
P. 14
Directed self-assembly software for single cell deposition
ware also addresses problems related to construct axis computer-controlled actuators for independent
scale-up, print speed, experimental conditions, and movement. Additional ancillary components, such as in
management of sensor data. The control software and situ energy meters and environmental (temperature and
the possibilities for integrated sensor data are presented. humidity) control, vary more widely between systems.
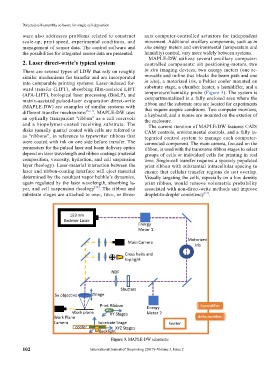
MAPLE-DW utilizes several ancillary computer-
2. Laser direct-write’s typical system controlled components: six positioning-motors, two
There are several types of LDW that rely on roughly in situ imaging devices, two energy meters (one re-
similar mechanisms for transfer and are incorporated movable and in-line that blocks the beam path and one
into comparable printing systems. Laser-induced for- in situ), a motorized iris, a Peltier cooler mounted on
ward transfer (LIFT), absorbing film-assisted LIFT substrate stage, a chamber heater, a humidifier, and a
(AFA-LIFT), biological laser processing (BioLP), and temperature/humidity probe (Figure 3). The system is
matrix-assisted pulsed-laser evaporation direct-write compartmentalized in a fully enclosed area where the
ribbon and the substrate area are located for experiments
(MAPLE-DW) are examples of similar systems with that require aseptic conditions. Two computer monitors,
different transfer mechanisms [8–11] . MAPLE-DW uses a keyboard, and a mouse are mounted on the exterior of
an optically transparent “ribbon” as a cell reservoir the enclosure.
and a biopolymer-coated receiving substrate. The The current iteration of MAPLE-DW features CAD/
disks (usually quartz) coated with cells are referred to CAM controls, environmental controls, and a fully in-
as “ribbons”, in reference to typewriter ribbons that te grated control system to manage each computer-
were coated with ink on one side before transfer. The connected component. The main camera, focused on the
parameters for the pulsed laser and beam delivery optics ribbon, is used with the transverse ribbon stages to select
depend on laser wavelength and ribbon coatings (material groups of cells or individual cells for printing in real
composition, viscosity, hydration, and cell suspension time. Single-cell transfer requires a sparsely populated
layer rheology). Laser-material interaction between the print ribbon with substantial intracellular spacing to
laser and ribbon-coating interface will eject material ensure that cellular transfer regions do not overlap.
determined by the resultant vapor bubble’s dynamics, Visually targeting the cells, especially on a low density
again regulated by the laser wavelength, absorbing la- print ribbon, would remove volumetric probability
yer, and cell suspension rheology [12] . The ribbon and associated with non-direct-write methods and improve
substrate stages are attached to one-, two-, or three- droplet-to-droplet consistency .
[13]
Figure 3. MAPLE-DW schematic
102 International Journal of Bioprinting (2017)–Volume 3, Issue 2