Page 163 - IJB-10-3
P. 163
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bone: Current & future
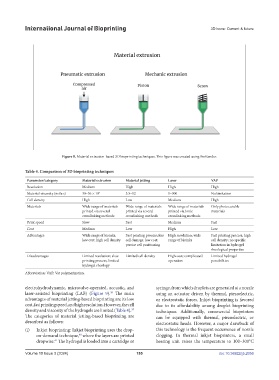
Figure 8. Material extrusion-based 3D bioprinting techniques. This figure was created using BioRender.
Table 4. Comparison of 3D bioprinting techniques
Parameter/category Material extrusion Material jetting Laser VAP
Resolution Medium High High High
Material viscosity (mPa·s) 30–36 × 10 7 3.5–12 1–300 No limitation
Cell density High Low Medium High
Materials Wide range of materials Wide range of materials Wide range of materials Only photocurable
printed via several printed via several printed via ionic materials
crosslinking methods crosslinking methods crosslinking methods
Print speed Slow Fast Medium Fast
Cost Medium Low High Low
Advantages Wide range of bioinks; Fast printing process; less High resolution; wide Fast printing process; high
low cost; high cell density cell damage; low cost; range of bioinks cell density; no specific
precise cell positioning limitation in hydrogel
rheological properties
Disadvantages Limited resolution; slow Limited cell density High cost; complicated Limited hydrogel
printing process; limited operation possibilities
hydrogel rheology
Abbreviation: VAP: Vat polymerization.
electrohydrodynamic, microvalve-operated, acoustic, and syringe, from which droplets are generated at a nozzle
laser-assisted bioprinting (LAB) (Figure 9). The main using an actuator driven by thermal, piezoelectric,
38
advantages of material jetting-based bioprinting are its low or electrostatic forces. Inkjet bioprinting is favored
cost, fast printing speed, and high resolution. However, the cell due to its affordability among droplet bioprinting
density and viscosity of the hydrogels are limited (Table 4). techniques. Additionally, commercial bioprinters
39
The categories of material jetting-based bioprinting are can be equipped with thermal, piezoelectric, or
described as follows: electrostatic heads. However, a major drawback of
(i) Inkjet bioprinting: Inkjet bioprinting uses the drop- this technology is the frequent occurrence of nozzle
on-demand technique, where the layers are printed clogging. In thermal inkjet bioprinters, a small
40
dropwise. The hydrogel is loaded into a cartridge or heating unit raises the temperature to 100–300°C
41
Volume 10 Issue 3 (2024) 155 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2056