Page 316 - IJB-10-3
P. 316
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-bioprinted hydrogel for pulp regeneration
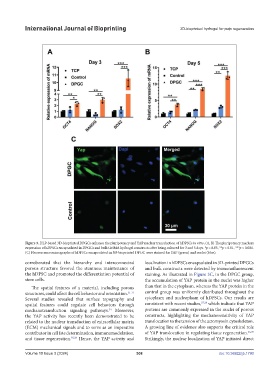
Figure 3. DLP-based 3D-bioprinted DPGCs enhance the pluripotency and YAP nuclear transduction of hDPSCs in vitro. (A, B) The pluripotency markers
expression of hDPSCs encapsulated in DPGCs and bulk GelMA hydrogel constructs after being cultured for 3 and 5 days. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
(C) Fluorescence micrographs of hDPSCs encapsulated in 3D-bioprinted DPGC were stained for YAP (green) and nuclei (blue).
corroborated that the hierarchy and interconnected localization in hDPSCs encapsulated in 3D-printed DPGCs
porous structure favored the stemness maintenance of and bulk constructs were detected by immunofluorescent
the hDPSC and promoted the differentiation potential of staining. As illustrated in Figure 3C, in the DPGC group,
stem cells. the accumulation of YAP protein in the nuclei was higher
The spatial features of a material, including porous than that in the cytoplasm, whereas the YAP protein in the
structures, could affect the cell behavior and orientation. 31-33 control group was uniformly distributed throughout the
Several studies revealed that surface topography and cytoplasm and nucleoplasm of hDPSCs. Our results are
spatial features could regulate cell behaviors through consistent with recent studies, 37,38 which indicate that YAP
mechanotransduction signaling pathways. Moreover, proteins are commonly expressed in the nuclei of porous
34
the YAP activity has recently been demonstrated to be constructs, highlighting the mechanosensitivity of YAP
related to the nuclear transduction of extracellular matrix translocation to the tension of the actomyosin cytoskeleton.
(ECM) mechanical signals and to serve as an imperative A growing line of evidence also supports the critical role
contributor in cell fate determination, immunomodulation, of YAP translocation in regulating tissue regeneration. 36,39
and tissue regeneration. 35,36 Hence, the YAP activity and Strikingly, the nuclear localization of YAP initiated direct
Volume 10 Issue 3 (2024) 308 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1790