Page 355 - IJB-10-3
P. 355
International Journal of Bioprinting hNVU chip for brain modeling and drug screening
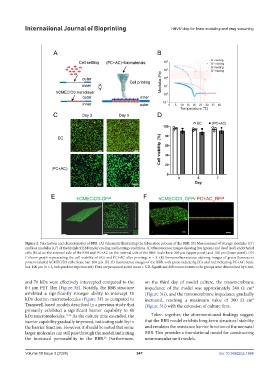
Figure 2. Fabrication and characteristics of BBB. (A) Schematic illustrating the fabrication process of the BBB. (B) Measurement of storage modulus (G’)
and loss modulus (G”) of the bioink of BBB under cooling and heating conditions. (C) Fluorescence images showing live (green) and dead (red) endothelial
cells (ECs) on the external side of the BBB and PC+AC on the internal side of the BBB. Scale bars: 200 μm (upper panel) and 100 μm (lower panel). (D)
Column graph representing the cell viability of ECs and PC+AC after printing, n = 3. (E) Immunofluorescence staining images of green fluorescent
protein-labeled hCMEC/D3 cells. Scale bar: 200 μm. (F) 3D fluorescence images of the BBB, with green indicating ECs and red indicating PC+AC. Scale
bar: 100 μm (n = 3, independent experiments). Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. Significant differences between the groups were determined by t-test.
and 70 kDa were effectively intercepted compared to the on the third day of model culture, the transmembrane
0.4 μm PET film (Figure 3E). Notably, the BBB structure impedance of the model was approximately 240 Ω cm
2
exhibited a significantly stronger ability to intercept 10 (Figure 3G), and the transmembrane impedance gradually
kDa dextran macromolecules (Figure 3F) as compared to increased, reaching a maximum value of 360 Ω cm
2
Transwell-based models described in a previous study that (Figure 3G) with the extension of culture time.
primarily exhibited a significant barrier capability to 40
kDa macromolecules. 31,32 As the culture time extended, the Taken together, the aforementioned findings suggest
barrier capability gradually improved, indicating stability in that the BBB model exhibits long-term structural stability
the barrier function. However, it should be noted that some and emulates the resistance barrier function of the neonatal
larger molecules can still pass through the model, indicating BBB. This provides a foundational model for constructing
the increased permeability in the BBB. Furthermore, neurovascular unit models.
20
Volume 10 Issue 3 (2024) 347 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1684