Page 504 - IJB-10-4
P. 504
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed variable stiffness scaffolds
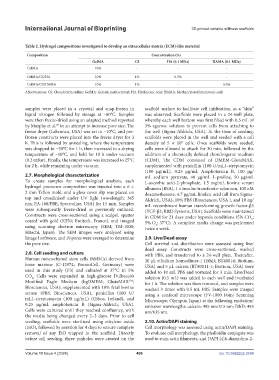
Table 2. Hydrogel compositions investigated to develop an extracellular matrix (ECM)-like material
Composition Concentration (%)
GelMA CS HA (0.1 MDa) HAMA (0.1 MDa)
GelMA 10% - - -
GelMA/CS/HA 10% 1% 0.5% -
GelMA/CS/HAMA 10% 1% - 0.5%
Abbreviations: CS: Chondroitin sulfate; GelMA: Gelatin methacryloyl; HA: Hyaluronic acid; HAMA: Methacrylated hyaluronic acid.
samples were placed in a cryovial and snap-frozen in scaffold surface to facilitate cell infiltration, as a “skin”
liquid nitrogen followed by storage at −80°C. Samples was observed. Scaffolds were placed in a 24-well plate,
were then freeze-dried using an adapted method reported whereby each well bottom was first filled with 0.5 mL of
by Murphy et al. in an attempt to increase pore size. The 3% agarose solution to prevent cells from attaching to
29
freeze dryer (Labconco, USA) was set to −10°C, and pre- the well (Sigma-Aldrich, USA). At the time of seeding,
frozen constructs were placed into the freeze dryer for 3 scaffolds were placed in the well and seeded with a cell
h. This is followed by annealing, where the temperature density of 5 × 10 cells. Once scaffolds were seeded,
5
was dropped to −30°C for 1 h, then increased to a drying cells were allowed to attach for 30 min, followed by the
temperature of −10°C, and held for 18 h under vacuum addition of a chemically defined chondrogenic medium
(0.2 mBar). Finally, the temperature was increased to 25°C (CDM). The CDM consisted of DMEM-GlutaMAX,
for 2 h, while remaining under vacuum. supplemented with penicillin (100 U/mL)–streptomycin
(100 μg/mL), 0.25 µg/mL Amphotericin B, 100 μg/
2.7. Morphological characterization mL sodium pyruvate, 40 μg/mL L-proline, 50 μg/mL
To create samples for morphological analysis, each L-ascorbic acid-2-phosphate, 1.5 mg/mL bovine serum
hydrogel precursor composition was injected into a 6 × albumin (BSA), 1 × insulin-transferrin-selenium, 100 nM
2 mm Teflon mold, and a glass cover slip was placed on dexamethasone, 4.7 µg/mL linoleic acid (all from Sigma-
top and crosslinked under UV light (wavelength: 365 Aldrich, USA), 10% FBS (Biosciences, USA ), and 10 ng/
nm; EA-160/FBE; Spectroline, USA) for 15 min. Samples mL recombinant human transforming growth factor-β3
were subsequently freeze-dried as previously outlined. (TGF-β3; R&D Systems, USA). Scaffolds were maintained
Constructs were cross-sectioned using a scalpel, sputter in CDM for 21 days under hypoxia conditions (5% CO ;
2
coated with gold (K550; Emitech, France), and imaged 5% O ; 37°C). A complete media change was performed
2
using scanning electron microscopy (SEM; TM-1000; twice a week.
Hitachi, Japan). The SEM images were analyzed using
Image J software, and 10 pores were averaged to determine 2.9. Live/Dead assay
the pore size. Cell survival and distribution were assessed using live/
dead assay. Constructs were cross-sectioned, washed
2.8. Cell seeding and culture with PBS, and transferred to a 24-well plate. Thereafter,
Human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) derived from 20 µL ethidium homodimer-1 (EthD; BT40014; Biotium,
bone marrow (C-12974; PromoCell, Germany) were USA) and 5 µL calcein (BT80011-1; Biotium, USA) were
used in this study (P3) and cultured at 37°C in 5% added to 10 mL PBS and vortexed for 3 min. Live/Dead
CO . Cells were expanded in high-glucose Dulbecco’s solution (0.5 mL) was added to each well and incubated
2
Modified Eagle Medium (hgDMEM; GlutaMAX ; for 1 h. The solution was then removed, and samples were
TM
Biosciences, USA), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine washed 3 times with 0.5 mL PBS. Samples were imaged
serum (FBS; Biosciences, USA), penicillin (100 U/ using a confocal microscope (FV-1000 Point Scanning
mL)–streptomycin (100 μg/mL) (Gibco, Ireland), and Microscope; Olympus, Japan) at the following excitation/
0.25 μg/mL amphotericin B (Sigma-Aldrich, USA). emission wavelengths: calcein: 495 nm/515 nm; EthD: 495
Cells were cultured until they reached confluency, with nm/635 nm.
the media being changed every 2–3 days. Prior to cell
seeding, scaffolds were sterilized using ethylene oxide 2.10. Actin/DAPI staining
(EtO), followed by aeration for 4 days to ensure complete Cell morphology was assessed using actin/DAPI staining.
removal of any EtO trapped in the scaffold. Directly To evaluate cell morphology, the phalloidin conjugate was
before cell seeding, three pinholes were created on the used to stain actin filaments, and DAPI (4’,6-diamidino-2-
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 496 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3784