Page 119 - IJB-10-5
P. 119
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting for organoid-derived EVs
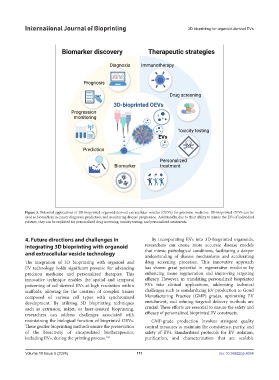
Figure 5. Potential applications of 3D-bioprinted organoid-derived extracellular vesicles (OEVs) for precision medicine. 3D-bioprinted OEVs can be
used as biomarkers in cancer diagnosis, prediction, and monitoring disease progression. Additionally, due to their ability to mimic the EVs of individual
patients, they can be exploited for personalized drug screening, toxicity testing, and personalized treatments.
4. Future directions and challenges in By incorporating EVs into 3D-bioprinted organoids,
integrating 3D bioprinting with organoid researchers can create more accurate disease models
and extracellular vesicle technology that mimic pathological conditions, facilitating a deeper
understanding of disease mechanisms and accelerating
The integration of 3D bioprinting with organoid and drug screening processes. This innovative approach
EV technology holds significant promise for advancing has shown great potential in regenerative medicine by
precision medicine and personalized therapies. This enhancing tissue regeneration and improving targeting
innovative technique enables the spatial and temporal efficacy. However, in translating personalized bioprinted
patterning of cell-derived EVs at high resolution within EVs into clinical applications, addressing technical
scaffolds, allowing for the creation of complex tissues challenges such as standardizing EV production to Good
composed of various cell types with synchronized Manufacturing Practice (GMP) grades, optimizing EV
development. By utilizing 3D bioprinting techniques enrichment, and refining targeted delivery methods are
such as extrusion, inkjet, or laser-assisted bioprinting, crucial. These efforts are essential to ensure the safety and
researchers can address challenges associated with efficacy of personalized bioprinted EV constructs.
maintaining the biological function of bioprinted OEVs. GMP-grade production involves stringent quality
These gentler bioprinting methods ensure the preservation control measures to maintain the consistency, purity, and
of the bioactivity of encapsulated biotherapeutics, safety of EVs. Standardized protocols for EV isolation,
including EVs, during the printing process. 162 purification, and characterization that are scalable
Volume 10 Issue 5 (2024) 111 doi: 10.36922/ijb.4054