Page 116 - IJB-10-5
P. 116
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting for organoid-derived EVs
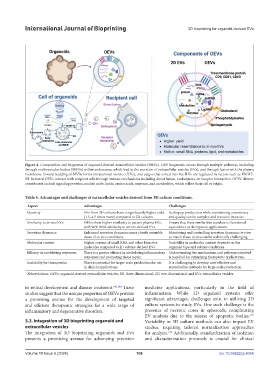
Figure 4. Composition and biogenesis of organoid-derived extracellular vesicles (OEVs). OEV biogenesis occurs through multiple pathways, including
through multivesicular bodies (MVBs) within endosomes, which lead to the secretion of extracellular vesicles (EVs), and through fusion with the plasma
membrane. Inward budding of MVBs forms intraluminal vesicles (ILVs), and cargos that sorted into the ILVs are regulated by factors such as ESCRT-
III. Released OEVs interact with recipient cells through various mechanisms including direct fusion, endocytosis, or receptor interaction. OEVs’ diverse
constituents include signaling proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, amino acids, enzymes, and metabolites, which reflect their cell of origin.
Table 4. Advantages and challenges of extracellular vesicles derived from 3D culture conditions.
Aspect Advantages Challenges
Quantity EVs from 3D cultures have a significantly higher yield Scaling up production while maintaining consistency
(1.5–4.5 times more) compared to 2D cultures. and quality can be complex and resource intensive.
Similarity to in vivo EVs OEVs show higher similarity to patient plasma EVs, Ensure that these similarities translate to functional
with 96% RNA similarity to serum-derived EVs. equivalence in therapeutic applications.
Secretion dynamics Enhanced secretion dynamics more closely resemble Monitoring and controlling secretion dynamics in vitro
those of in vivo conditions. to match those in vivo can be technically challenging.
Molecular content Higher content of small RNA and other bioactive Variability in molecular content depends on the
molecules compared to 2D culture-derived EVs. organoid type and culture conditions.
Efficacy in modulating responses There is a greater efficacy in modulating inflammatory Understanding the mechanisms and pathways involved
responses and promoting tissue repair. is required for optimizing therapeutic applications.
Scalability for therapeutics There is potential for larger-scale production for use It is challenging to develop cost-effective and
in clinical applications. reproducible methods for large-scale production.
Abbreviations: OEVs, organoid-derived extracellular vesicles; 3D, three-dimensional; 2D, two-dimensional; and EVs, extracellular vesicles.
in retinal development and disease treatment. 143,144 These medicine applications, particularly in the field of
studies suggest that the unique properties of OEVs provide inflammation. While 3D organoid systems offer
a promising avenue for the development of targeted significant advantages, challenges exist in utilizing 3D
and efficient therapeutic strategies for a wide range of culture systems to study EVs. One such challenge is the
inflammatory and degenerative disorders. presence of necrotic cores in spheroids, complicating
EV analysis due to the release of apoptotic bodies.
145
3.3. Integration of 3D bioprinting organoid and Variability in 3D culture methods can also impact EV
extracellular vesicles studies, requiring tailored normalization approaches
The integration of 3D bioprinting organoids and EVs for analysis. Additionally, standardization of isolation
146
presents a promising avenue for advancing precision and characterization protocols is crucial for clinical
Volume 10 Issue 5 (2024) 108 doi: 10.36922/ijb.4054