Page 403 - IJB-10-5
P. 403
International Journal of Bioprinting DEX-Loaded PLGA microspheres enhance cartilage regeneration
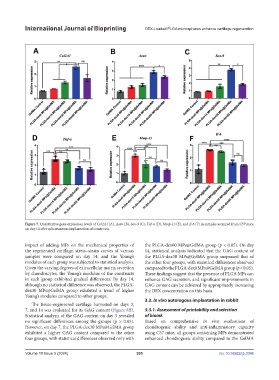
Figure 7. Quantitative gene expression levels of Col2A1 (A), Acan (B), Sox-9 (C), Tnf-α (D), Mmp-13 (E), and Il-6 (F) in samples acquired from C57 mice
on day 14 after subcutaneous implantation of constructs.
impact of adding MPs on the mechanical properties of the PLGA-dex60 MPs@GelMA group (p < 0.05). On day
the regenerated cartilage, stress–strain curves of various 14, statistical analysis indicated that the GAG content of
samples were compared on day 14, and the Young’s the PLGA-dex30 MPs@GelMA group surpassed that of
modulus of each group was subjected to statistical analysis. the other four groups, with statistical differences observed
Given the varying degrees of extracellular matrix secretion compared to the PLGA-dex0 MPs@GelMA group (p < 0.05).
by chondrocytes, the Young’s modulus of the constructs These findings suggest that the presence of PLGA MPs can
in each group exhibited gradual differences. By day 14, enhance GAG secretion, and significant improvements in
although no statistical difference was observed, the PLGA- GAG content can be achieved by appropriately increasing
dex30 MPs@GelMA group exhibited a trend of higher the DEX concentration on this basis.
Young’s modulus compared to other groups.
3.3. In vivo autologous implantation in rabbit
The tissue-engineered cartilage harvested on days 3,
7, and 14 was evaluated for its GAG content (Figure 8B). 3.3.1. Assessment of printability and selection
Statistical analysis of the GAG content on day 3 revealed of bioink
no significant differences among the groups (p > 0.05). Based on comprehensive in vivo evaluations of
However, on day 7, the PLGA-dex30 MPs@GelMA group chondrogenic ability and anti-inflammatory capacity
exhibited a higher GAG content compared to the other using C57 mice, all groups containing MPs demonstrated
four groups, with statistical differences observed only with enhanced chondrogenic ability compared to the GelMA
Volume 10 Issue 5 (2024) 395 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3396