Page 501 - IJB-10-5
P. 501
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting of full-thickness skin with a rete ridge structure
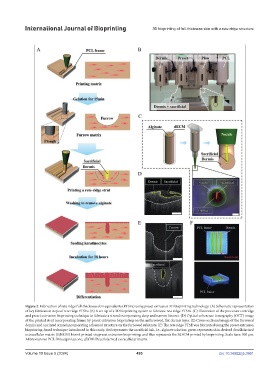
Figure 2. Fabrication of rete ridge full-thickness skin equivalents (FTSEs) using preset extrusion 3D bioprinting technology. (A) Schematic representation
of key fabrication steps of rete ridge FTSEs. (B) A set-up of a 3D bioprinting system to fabricate rete ridge FTSEs. (C) Illustration of the precursor cartridge
and preset extrusion bioprinting technique to fabricate a strand incorporating deep and narrow fissures. (D) Optical coherence tomography (OCT) image
of the printed strut incorporating fissure by preset extrusion bioprinting on the unfurrowed, flat dermis layer. (E) Cross-sectional image of the furrowed
dermis and a printed strand incorporating a fissured structure on the furrowed substrate. (F) The rete ridge FTSE was fabricated using the preset extrusion
bioprinting-based technique introduced in this study. Red represents the sacrificial ink, i.e., alginate solution; green represents skin-derived decellularized
extracellular matrix (SdECM) bioink printed via preset extrusion bioprinting; and blue represents the SdECM printed by bioprinting. Scale bars: 500 μm.
Abbreviations: PCL: Polycaprolactone; dECM: Decellularized extracellular matrix.
Volume 10 Issue 5 (2024) 493 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3961