Page 26 - IJB-10-6
P. 26
International Journal of Bioprinting Bioprinting for wearable tech and robot
to significant advancements in treating neurological promises a future wherein assistive devices seamlessly
disorders, enhancing cognitive abilities, and restoring harmonize with the human body, blurring the lines
function to individuals with spinal cord injuries. between biological and mechanical components and
Bioprinting also ensures compatibility and minimizes the function (Figure 2). 20
potential for immune rejection. Such interdisciplinary Bioprinting is established on a comprehensive
16
integration is poised to redefine the boundaries of multidisciplinary framework, offering significant benefits
human-machine interaction and explore new frontiers in for the advancement of various fields. In this review,
enhancing human capabilities. we first introduce the methodologies, materials, and
The advancement of bioprinting in bone research instrumental equipment that constitute the development
suggests that it could provide new approaches of bioprinting. Thereafter, we discuss the association of
for fabricating user-friendly exoskeleton robots. bioprinting with wearable sensors, BMIs, and exoskeleton
Exoskeleton robotics, an intriguing subset of robots. For wearable technology, we analyze the current
biomechatronics, pertains to the design, development, and prospective contributions of bioprinting to the
and deployment of wearable robotic apparatus that are development of electronic skin and body area networks
in sync with the intents and movements of the human based on the utilization of bioprinted bionic skin. Similarly,
body. These devices are meticulously engineered to we investigate the prospects of bioprinting with exoskeleton
17
augment, assist, enable, or enhance physical activity and humanoid robots, based on current evidence on
through direct interaction with the limbs or other body bioprinted bone and cartilage. Finally, anchored on the
parts. Exoskeleton robotics stands to benefit from the utilization of bioprinted nerve conduits, we elaborate on
advances in bioprinting as well. Ideally, lightweight, the prospects of bioprinting technology to advance BMIs
18
adaptive exoskeletons with “bio-actuators” are capable and neuromorphic systems. This review is the first to
of responsive and organic movements that mimic explore bioprinting applications across diverse cutting-
natural muscle contractions. These innovations could edge fields. Although interdisciplinary studies are still at
transform rehabilitation therapies and enhance mobility a nascent stage, bioprinting technology could potentially
for individuals with impairments. The integration of serve as the key link between carbon-based and silicon-
19
biologically inspired printing and robotic exoskeletons based life forms.
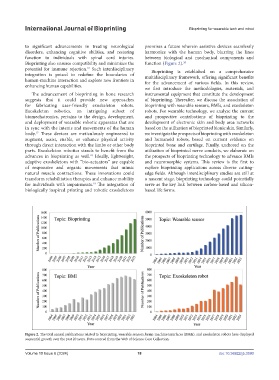
Figure 2. The total annual publications related to bioprinting, wearable sensors, brain-machine interfaces (BMIs), and exoskeleton robots have displayed
sequential growth over the past 20 years. Data sourced from the Web of Science Core Collection.
Volume 10 Issue 6 (2024) 18 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3590