Page 376 - IJB-10-6
P. 376
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed NAFLD model
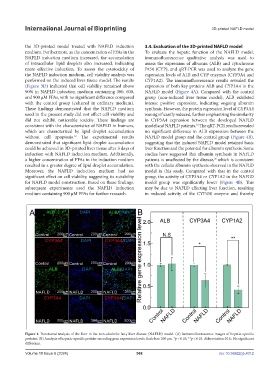
the 3D-printed model treated with NAFLD induction 3.4. Evaluation of the 3D-printed NAFLD model
medium. Furthermore, as the concentration of FFAs in the To evaluate the hepatic function of the NAFLD model,
NAFLD induction medium increased, the accumulation immunofluorescence qualitative analysis was used to
of intracellular lipid droplets also increased, indicating assess the expression of albumin (ALB) and cytochrome
more effective induction. To assess the cytotoxicity of P450 (CYP), and qRT-PCR was used to analyze the gene
the NAFLD induction medium, cell viability analysis was expression levels of ALB and CYP enzymes (CYP3A4 and
performed on the induced liver tissue model. The results CYP1A2). The immunofluorescence results revealed the
(Figure 3D) indicated that cell viability remained above expression of both key proteins ALB and CYP3A4 in the
90% in NAFLD induction medium containing 300, 600, NAFLD model (Figure 4A). Compared with the control
and 900 μM FFAs, with no significant difference compared group (non-induced liver tissue model), ALB exhibited
with the control group (cultured in ordinary medium). intense positive expression, indicating ongoing albumin
These findings demonstrated that the NAFLD medium synthesis. However, the protein expression level of CYP3A4
used in the present study did not affect cell viability and was significantly reduced, further emphasizing the similarity
did not exhibit noticeable toxicity. These findings are in CYP3A4 expression between the developed NAFLD
consistent with the characteristics of NAFLD in humans, model and NAFLD patients. The qRT-PCR results revealed
33
which are characterized by lipid droplet accumulation no significant difference in ALB expression between the
without cell apoptosis. The experimental results NAFLD model group and the control group (Figure 4B),
32
demonstrated that significant lipid droplet accumulation suggesting that the induced NAFLD model retained basic
could be achieved in 3D-printed liver tissue after 3 days of liver function and the potential for albumin synthesis. Some
induction with NAFLD induction medium. Additionally, studies have suggested that albumin synthesis in NAFLD
26
a higher concentration of FFAs in the induction medium patients is unaffected by the disease, which is consistent
resulted in a greater degree of lipid droplet accumulation. with the cellular albumin synthesis observed in the NAFLD
Moreover, the NAFLD induction medium had no model in this study. Compared with that in the control
significant effect on cell viability, suggesting its suitability group, the activity of CYP3A4 or CYP1A2 in the NAFLD
for NAFLD model construction. Based on these findings, model group was significantly lower (Figure 4B). This
subsequent experiments used the NAFLD induction may be due to NAFLD affecting liver function, resulting
medium containing 900 μM FFAs for further research. in reduced activity of the CYP450 enzyme and thereby
Figure 4. Functional analysis of the liver in the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) model. (A) Immunofluorescence images of hepatic-specific
proteins. (B) Analysis of hepatic-specific protein-encoding gene expression levels. Scale bar: 200 µm. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. Abbreviation: N.S.: No significant
difference.
Volume 10 Issue 6 (2024) 368 doi: 10.36922/ijb.4312