Page 382 - IJB-10-6
P. 382
International Journal of Bioprinting Innovative manufacturing of ω-3-enriched chocolate
1. Introduction food are thoroughly cleaned, 3D-printed food can exhibit
a longer shelf life than conventionally prepared food.
3
3D printing, also referred to as additive manufacturing, Numerous 3D-printed foods have been created, ranging
for food applications is growing in popularity in terms of from savory dishes to sugary sweets; simple shapes and
fundamental research and commercial efforts. It has been intricate designs have been demonstrated. Biodegradable
favored for industrial and biomedical applications due to its cups with 3D-printed poly-capsules of energy drink
unique ability to create 3D objects with geometries based ingredients; plant-based meats that mimic the nutritional
on a digital design in a layer-by-layer manner. In terms of properties, texture, taste, and appearance of animal-based
fabrication efforts, it is possible to separate raw materials meat products; cereal-based snacks that are enriched with
into printable and non-printable foods; alternative edible insects; 3D food structures made out of sugars with
resources, such as microorganisms, can serve as raw a variety of flavors, such as chocolate, watermelon, cherry,
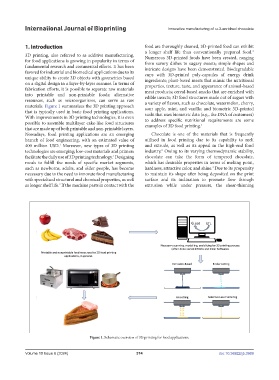
materials. Figure 1 summarizes the 3D printing approach sour apple, mint, and vanilla; and biometric 3D-printed
that is typically used in basic food printing applications. sushi that uses biometric data (e.g., the DNA of customers)
With improvements in 3D printing technologies, it is even to address specific nutritional requirements are some
possible to assemble multilayer cake-like food structures examples of 3D food printing. 1
that are made up of both printable and non-printable layers.
Nowadays, food printing applications are an emerging Chocolate is one of the materials that is frequently
branch of food engineering, with an estimated value of utilized in food printing due to its capability to melt
400 million USD. Moreover, new types of 3D printing and extrude, as well as its appeal in the high-end food
1
technologies are emerging; low-cost materials and printers industry. Owing to its varying thermodynamic stability,
2
facilitate the daily use of 3D printing technology. Designing chocolate can take the form of tempered chocolate,
1
meals to fulfill the needs of specific market segments, which has desirable properties in terms of melting point,
4
such as newborns, adults, and older people, has become hardness, attractive color, and shine. Due to its propensity
necessary due to the need to innovate food manufacturing to maintain its shape after being deposited on the print
with specialized structural and chemical properties, as well surface and its inclination to promote flow through
as longer shelf life. If the machine parts in contact with the extrusion while under pressure, the shear-thinning
2
Figure 1. Schematic overview of 3D printing for food applications.
Volume 10 Issue 6 (2024) 374 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3969