Page 49 - IJB-10-6
P. 49
International Journal of Bioprinting Semi-solid extrusion for pediatric medicine
Additive manufacturing (AM) processes offer several 2. Additive manufacturing processes
advantages over traditional methods. They enable complex for drugs
objects to be manufactured with high precision and
enable flexible modifications to the object’s characteristics 2.1. Processes overview
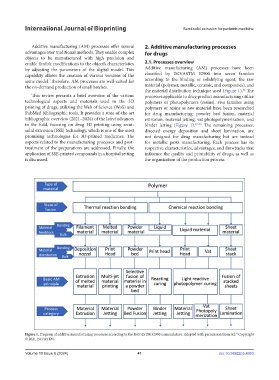
by adjusting the parameters of the digital model. This Additive manufacturing (AM) processes have been
capability allows the creation of various versions of the classified by ISO/ASTM 52900 into seven families
same model. Therefore, AM processes are well-suited for according to the binding or solidifying agent, the raw
the on-demand production of small batches. material (polymer, metallic, ceramic, and composites), and
the material distribution technique used (Figure 1). The
56
This review presents a brief overview of the various processes applicable to drug product manufacturing utilize
technological aspects and materials used in the 3D polymers or photopolymers (resins). Five families using
printing of drugs, utilizing the Web of Science (WoS) and polymers or resins as raw material have been researched
PubMed bibliographic tools. It provides a state-of-the-art for drug manufacturing: powder bed fusion, material
bibliographic overview (2021–2024) of the latest advances extrusion, material jetting, vat photopolymerization, and
in the field, focusing on drug 3D printing using semi- binder jetting (Figure 1). 57–59 The remaining processes,
solid extrusion (SSE) technology, which is one of the most directed energy deposition and sheet lamination, are
promising technologies for 3D-printed medicines. The not designed for drug manufacturing but are instead
aspects related to the manufacturing processes and post- for metallic parts manufacturing. Each process has its
treatment of the preparations are addressed. Finally, the respective characteristics, advantages, and drawbacks that
application of SSE-printed compounds in a hospital setting influence the quality and printability of drugs, as well as
is discussed. the organization of the production process.
Figure 1. Diagram of additive manufacturing processes according to the ISO/ASTM 52900 nomenclature. Adapted with permission from ref. Copyright
52
© 2021 ISO/ASTM.
Volume 10 Issue 6 (2024) 41 doi: 10.36922/ijb.4063