Page 17 - IJB-7-4
P. 17
Zhuang, et al.
Ref [136] [134] [133] [140] [124] [125] [126]
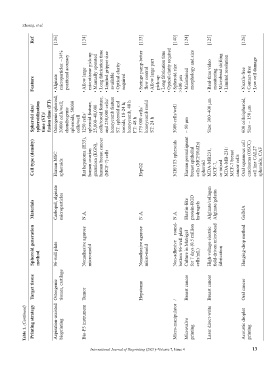
microparticles: ~34% positional accuracy microtissue pick-up • Manually operated Long fabrication time Limited gripper size Optical clarity Syringe pump-better Allow large part • Long fabrication time Optical clarity required Spheroid size morphology and size Real-time video • Microbead shifting • Limited resolution • Low cell damage
Feature Alginate • Allow large • • • available • required • flow control • pick-up • • >300 μm Maintained • • monitoring • Nozzle-free • Contact-free
Spheroid size/ spheroidization time (ST)/ fusion time (FT) Osteogenic spheroid, 20000 cells/well; chondrogenic spheroids, 50000 cells/well 1250 cells/ spheroid feature, 25,000–40,000 cells/toroid feature, and 250,000 cells/ honeycomb feature ST: spheroid and toroids, 18-24 h; honeycomb, 48 h FT: 48 h 375 000 cells/ honeycomb mold ST: 24 h 3000 cells/well ~ 50 μm Size: 300–400 μm 600 cells/spheroid, Size ~ 150 μm
Cell type (density) Human MSC spheroids Rat hepatoma (H35), human ovarian granulosa (KGN), human breast cancer (MCF-7) cells HepG2 NIH/3T3 spheroids Human premalignant breast epithelial cells (MCF10ATs) spheroid MDA-MB231, MCF-7, or mixed MDA-MB-231/ MCF-7 breast cancer cells Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cell line CAL27 spheroids, CAF
Materials Carbopol, alginate microparticles N.A. N.A. N.A. Elastin-like protein-RGD hydrogels Alginate/collagen Alginate/gelatin GelMA
Spheroid generation method 96-well plate Nonadhesive agarose micro-mold Nonadhesive agarose micro-mold Non-adhesive round- bottom 96-well plate Culture in Matrigel for 7 days (0.5 million cells/mL) High-voltage electric field-driven microbead fabrication Hanging-drop method
Target tissue Osteogenic tissues, cartilage Tumor Hepatoma / Breast cancer Breast cancer Oral cancer
Table 1. (Continued) Printing strategy Aspiration-assisted bioprinting Bio-P3 instrument Micro-manipulator Microvalve printing Laser direct-write Acoustic droplet printing
International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 4 13