Page 7 - IJB-7-4
P. 7
Zhuang, et al.
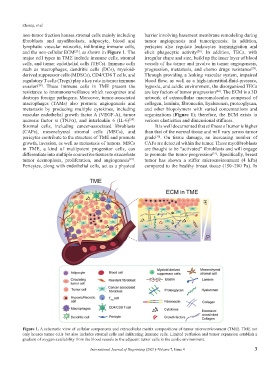
non-tumor fraction houses stromal cells mainly including barrier involving basement membrane remodeling during
fibroblasts and myofibrolasts, adipocyte, blood and tumor angiogenesis and tumorigenesis. In addition,
lymphatic vascular networks, infiltrating immune cells, pericytes also regulate leukocytes transmigration and
and the non-cellular ECM , as shown in Figure 1. The elicit phagocytic activity . In addition, TECs, with
[28]
[23]
major cell types in TME include immune cells, stromal irregular shape and size, build up the inner layer of blood
cells, and tumor endothelial cells (TECs). Immune cells vessels of the tumor and involve in tumor angiogenesis,
such as macrophages, dendritic cells (DCs), myeloid- progression, metastasis, and chemo drugs resistance .
[29]
derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), CD4/CD8 T cells, and Through providing a leaking vascular system, impaired
regulatory T cells (Tregs) play a key role in tumor immune blood flow, as well as a high-interstitial-fluid-pressure,
evasion . These immune cells in TME present the hypoxia, and acidic environment, the disorganized TECs
[26]
resistance to immunosurveillance which recognizes and are key factors of tumor progression . The ECM is a 3D
[24]
destroys foreign pathogens. Moreover, tumor-associated network of extracellular macromolecules composed of
macrophages (TAMs) also promote angiogenesis and collagen, laminin, fibronectin, hyaluronan, proteoglycan,
metastasis by producing multiple cytokines, including and other biopolymers with varied concentrations and
vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A), tumor organizations (Figure 1); therefore, the ECM exists in
necrosis factor α (TNFα), and interleukin 6 (IL-6) . various elasticities and dimensional stiffness.
[24]
Stromal cells, including cancer-associated fibroblasts It is well documented that stiffness of tumor is higher
(CAFs), mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs), and than that of the normal tissue and will vary across tumor
pericytes contribute to the structure of TME and promote grade . On tissue damage, an increasing number of
[30]
growth, invasion, as well as metastasis of tumors. MSCs CAFs are detected within the tumor. These myofibroblasts
in TME, a kind of multipotent progenitor cells, can are thought to be “activated” fibroblasts and will engage
differentiate into multiple connective tissues to exacerbate to promote the tumor progression . Specifically, breast
[31]
tumor desmoplasia, proliferation, and angiogenesis . tumor has shown a stiffer microenvironment (4 kPa)
[27]
Pericytes, along with endothelial cells, act as a physical compared to the healthy breast tissue (150~200 Pa). In
Figure 1. A schematic view of cellular components and extracellular matrix compositions of tumor microenvironment (TME). TME not
only houses tumor cells but also includes stromal cells and infiltrating immune cells. Limited perfusion and tumor expansion establish a
gradient of oxygen availability from the blood vessels to the adjacent tumor cells in the acidic environment.
International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 4 3