Page 85 - IJB-8-1
P. 85
Liu, et al.
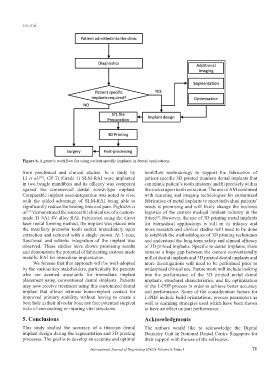
Figure 6. A generic workflow for using patient-specific implants in dental applications.
from preclinical and clinical studies. In a study by workflow methodology to support the fabrication of
Li et al. , CP-Ti (Grade 1) SLM-RAI were implanted patient-specific 3D printed titanium dental implants that
[29]
in two beagle mandibles and its efficacy was compared can mimic patient’s tooth anatomy and fit precisely within
against the commercial dental screw-type implant. the socket upon tooth extraction. The use of AM combined
Comparable implant osseointegration was noted in vivo, with scanning and imaging technologies for customized
with the added advantage of SLM-RAI being able to fabrication of metal implants to meet individual patients’
significantly reduce the healing time and pain. Figliuzzi et needs is promising and will likely change the business
al. demonstrated the successful clinical use of a custom- logistics of the current medical implant industry in the
[12]
made Ti–6Al–4V alloy RAI. Fabricated using the direct future . However, the use of 3D printing metal implants
[5]
laser metal forming method, the implant was placed into for biomedical applications is still in its infancy and
the maxillary premolar tooth socket immediately upon more research and clinical studies will need to be done
extraction and restored with a single crown. At 1-year, to establish the methodologies of 3D printing techniques
functional and esthetic integration of the implant was and understand the long-term safety and clinical efficacy
observed. These studies have shown promising results of 3D printed implants. Specific to dental implants, there
and demonstrate the potential of fabricating custom-made remains a huge gap between the current conventionally
metallic RAI for immediate implantation. milled dental implants and 3D printed dental implants and
We foresee that this approach will be well-adopted more investigations will need to be performed prior to
by the various key stakeholders, particularly for patients widespread clinical use. Future work will include looking
who are deemed unsuitable for immediate implant into the performance of the 3D printed metal dental
placement using conventional dental implants. Patients implants, structural characteristics, and the optimization
may now receive treatment using this customized dental of the L-PBF process in order to achieve better accuracy
implant that allows intimate bone-implant contact for and performance. Some of the consideration factors for
improved primary stability, without having to create a L-PBF include build orientations, process parameters as
bore hole in their alveolar bone nor face potential surgical well as scanning strategies used which have been shown
risks of encroaching or injuring vital structures. to have an effect on part performance.
5. Conclusions Acknowledgments
This study studied the accuracy of a titanium dental The authors would like to acknowledge the Digital
implant design during the segmentation and 3D printing Dentistry Unit in National Dental Centre Singapore for
processes. The goal is to develop an accurate and optimal their support with the use of the softwares.
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 1 71