Page 169 - IJB-8-2
P. 169
Yi-Wu, et al.
A B A
C D
B
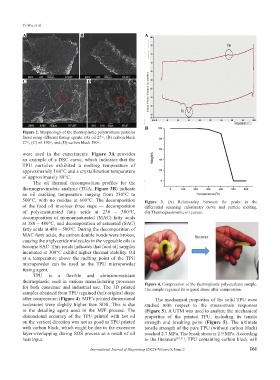
Figure 2. Morphology of the thermoplastic polyurethane particles
fused using different fusing agents: (A) oil 27×, (B) carbon black
27×, (C) oil 190×, and (D) carbon black 190×.
were used in the experiments. Figure 3A provides
an example of a DSC curve, which indicates that the
TPU particles exhibited a melting temperature of
approximately 160°C and a crystallization temperature
of approximately 80°C.
The oil thermal decomposition profiles for the
thermogravimetric analysis (TGA; Figure 3B) indicate
an oil cracking temperature ranging from 230°C to
500°C, with no residue at 600°C. The decomposition Figure 3. (A) Relationship between the peaks in the
of the food oil involves three steps — decomposition differential scanning calorimetry curve and particle melting.
of polyunsaturated fatty acids at 230 – 380°C, (B) Thermogravimetric oil curves.
decomposition of monounsaturated (MAC) fatty acids
at 380 – 480°C, and decomposition of saturated (SAC)
fatty acids at 480 – 500ºC. During the decomposition of
MAC fatty acids, the carbon double bonds were broken,
causing the triglyceride molecules in the vegetable oils to
become SAC. This result indicates that food oil samples
incubated at 300°C exhibit higher thermal stability. Oil
at a temperature above the melting point of the TPU
micropowder can be used as the TPU micropowder
fusing agent.
TPU is a flexible and abrasion-resistant
thermoplastic used in various manufacturing processes Figure 4. Compression of the thermoplastic polyurethane sample.
for both consumer and industrial use. The 3D printed The sample regained its original shape after compression.
samples obtained from TPU regained their original shape
after compression (Figure 4). MJF’s printed dimensional The mechanical properties of the solid TPU were
accuracies were slightly higher than SOS. This is due studied with respect to the stress-strain responses
to the detailing agent used in the MJF process. The (Figure 5). A UTM was used to analyze the mechanical
dimensional accuracy of the TPU printed with hot oil properties of the printed TPU, including its tensile
on the vertical direction was not as good as TPU printed strength and breaking point (Figure 5). The ultimate
with carbon black, which might be due to the excessive tensile strength of the pure TPU (without carbon black)
layer-overlapping during SOS process as a result of oil reached 2.7 MPa. The break stress is 2.9 MPa. According
heat input. to the literature [10,11] , TPU containing carbon black will
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 2 161