Page 242 - IJB-8-3
P. 242
3D Printing and Vascularized Organ Construction
(ECMs). The outermost layer, adventitia, is composed of
fibroblasts, nerve fibers, and ECMs with a lot of collagen,
which can effectively maintain vascular morphology
and increase vascular elasticity. The middle membrane,
tunica media (or elastica), is mainly composed of smooth
muscle cells and pericytes. It has unique cardiac protective
functions such as angiogenesis and chronic inflammation
alleviation with the thickest structure. The innermost
layer, intima, is mainly consisted of ECs, which plays
an important role in regulating blood flow, platelet, and
blood cell function .
[16]
2.2. Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis
In human body, neovascularization is the formation of
functional microvascular networks with red blood cell
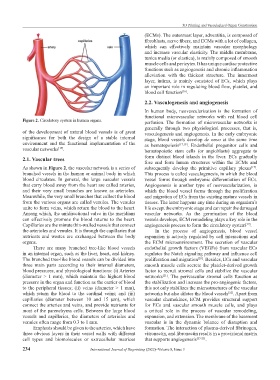
Figure 2. Circulatory system in human organs. perfusion. The formation of microvascular networks is
generally through two physiological processes, that is,
of the development of natural blood vessels is of great vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. In the early embryonic
significance for both the design of a stable internal stage, blood vessels develop de novo at the same time
environment and the functional implementation of the as hematopoiesis [17,18] . Endothelial progenitor cells and
vascular networks . hematopoietic stem cells (or angioblasts) aggregate to
[15]
2.1. Vascular trees form distinct blood islands in the liver. ECs gradually
fuse and form lumen structures within the ECMs and
As shown in Figure 2, the vascular network is a series of subsequently develop the primitive capillary plexus .
[17]
branched vessels in the human or animal body in which This process is called vasculogenesis, in which the blood
blood circulates. In general, the large vascular vessels vessel forms through embryonic differentiation of ECs.
that carry blood away from the heart are called arteries, Angiogenesis is another type of neovascularization, in
and their very small branches are known as arterioles. which the blood vessel forms through the proliferation
Meanwhile, the very small branches that collect the blood and migration of ECs from the existing mature vessels in
from the various organs are called venules. The venules tissues. The latter happens any time during an organism’s
unite to form veins, which return the blood to the heart. life except the embryonic stage and can repair the damaged
Among which, the unidirectional valve in the meridians vascular networks. As the germination of the blood
can effectively promote the blood returns to the heart. vessels develops, ECM remodeling plays a key role in the
Capillaries are the minute thin-walled vessels that connect angiogenesis process to form the circulatory system .
[19]
the arterioles and venules. It is through the capillaries that In the process of angiogenesis, blood vessel
nutrients and wastes are exchanged between the body expansion is actively regulated by cell interactions and
organs. the ECM microenvironment. The secretion of vascular
There are many branched tree-like blood vessels endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) from vascular ECs
in an internal organ, such as the liver, heart, and kidney. regulates the Notch signaling pathway and influence cell
The branched tree-like blood vessels can be divided into proliferation and migration . Besides, ECs and vascular
[20]
three main parts according to their internal diameters, smooth muscle cells secrete the platelet-derived growth
blood pressures, and physiological functions: (i) Arteries factor to recruit stromal cells and stabilize the vascular
(diameter > 1 mm), which maintain the highest blood networks . The perivascular stromal cells function as
[21]
pressure in the organ and function as the carrier of blood the stabilization and increase the pro-angiogenic factors,
to the peripheral tissues; (ii) veins (diameter > 1 mm), this not only stabilizes the microstructures of the vascular
which return the blood to the cardinal veins; and (iii) networks but also dilates the blood vessels . Apart from
[22]
capillaries (diameter between 10 and 15 μm), which vascular chemokines, ECM provides structural support
connect the arteries and veins, and provide nutrients for for ECs and vascular smooth muscle cells, and plays
most of the parenchyma cells. Between the large blood a critical role in the process of vascular remodeling,
vessels and capillaries, the diameters of arterioles and expansion, and extension. The membrane of the basement
venules often range from 0.3 to 1 mm. vascular is in the dynamic balance of disruption and
Emphasis should be given to the arteries, which have formation. The interaction of plasma-derived fibrinogen,
three obvious layers in their vessel walls with different vitronectin, and fibronectin results in a provisional matrix
cell types and biomolecules or extracellular matrices that supports angiogenesis [23-25] .
234 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 3