Page 109 - IJB-9-1
P. 109
International Journal of Bioprinting Robotic in situ bioprinting
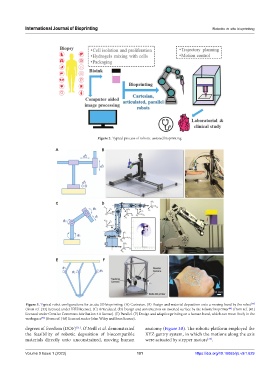
Figure 2. Typical process of robotic-assisted bioprinting.
A B
C D
E F
[33]
Figure 3. Typical robot configurations for in situ 3D bioprinting. (A) Cartesian. (B) Design and material deposition onto a moving hand by the robot
(from ref. [33] licensed under IEEE license). (C) Articulated. (D) Design and construction on inverted surface by the robotic bioprinter (from ref. [41]
[41]
licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 license). (E) Parallel. (F) Design and adaptive printing on a human hand, which can move freely in the
[46]
workspace (from ref. [46] licensed under John Wiley and Sons license).
degrees of freedom (DOF) . O’Neill et al. demonstrated anatomy (Figure 3B). The robotic platform employed the
[31]
the feasibility of robotic deposition of biocompatible XYZ gantry system, in which the motions along the axis
materials directly onto unconstrained, moving human were actuated by stepper motors .
[33]
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2023) 101 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i1.629