Page 123 - IJB-9-1
P. 123
International Journal of Bioprinting Fabrication of 3D breast tumor model for drug screening
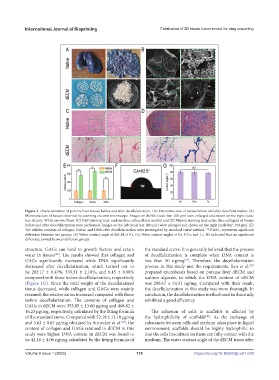
Figure 1. Characterization of porcine liver tissues before and after decellularization. (A) Macrostructure of tissues before and after decellularization. (B)
Microstructure of tissues observed by scanning electron microscope. Images on the left (scale bar: 100 μm) were enlarged and shown on the right (scale
bar: 50 μm). White arrows: fibers. (C) H&E staining (red: nuclear; blue: extracellular matrix) and (D) Masson staining (red: actin; blue: collagen) of tissues
before and after decellularization were performed. Images on the left (scale bar: 400 μm) were enlarged and shown on the right (scale bar: 100 μm). (E)
The relative contents of collagen, GAGs, and DNA after decellularization were investigated by standard curve method. **P<0.01, represents significant
difference between two groups. (F) Water contact angle of dECM at 0 s. (G) Water contact angles at 0 s, 0.5 s, and 1 s. NS indicated that no significant
difference existed between different groups.
structure, GAGs can bind to growth factors and retain the standard curve. It is generally believed that the process
water in tissues . The results showed that collagen and of decellularization is complete when DNA content is
[45]
GAGs significantly increased while DNA significantly less than 50 ng/mg . Therefore, the decellularization
[16]
decreased after decellularization, which turned out to process in this study met the requirements. Sun et al.
[47]
be 283.17 ± 0.47%, 333.31 ± 2.18%, and 6.45 ± 0.68% prepared microbeads based on porcine liver dECM and
compared with those before decellularization, respectively sodium alginate, in which the DNA content of dECM
(Figure 1G). Since the total weight of the decellularized was 290.67 ± 54.31 ng/mg. Compared with their result,
tissue decreased, while collagen and GAGs were mainly the decellularization in this study was more thorough. In
retained, the relative ratios increased compared with those conclusion, the decellularization method used in this study
before decellularization. The contents of collagen and exhibited a good efficiency.
GAGs in dECM were 353.85 ± 13.60 μg/mg and 468.82 ±
16.23 μg/mg, respectively, calculated by the fitting formula The adhesion of cells to scaffolds is affected by
of the standard curve. Compared with 52.19 ± 11.18 μg/mg the hydrophilicity of scaffolds . As the exchange of
[48]
and 5.62 ± 0.65 μg/mg obtained by Struecker et al. , the substances between cells and medium takes place in liquid
[46]
content of collagen and GAGs retained in dECM in this environment, scaffolds should be highly hydrophilic so
study were higher. DNA content in dECM was found to that the cells inoculated on them can fully contact with the
be 42.16 ± 4.06 ng/mg calculated by the fitting formula of medium. The water contact angle of the dECM tissue after
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2023) 115 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i1.630