Page 125 - IJB-9-1
P. 125
International Journal of Bioprinting Fabrication of 3D breast tumor model for drug screening
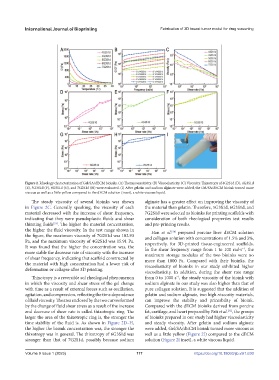
Figure 2. Rheology characterization of Gel/SA/dECM bioinks. (A) Thermosensitivity. (B) Viscoelasticity. (C) Viscosity. Thixotropy of 4G2S1d (D), 4G3S1d
(E), 5G3S1d (F), 6G3S1d (G), and 7G2S1d (H) were evaluated. (I) After gelatin and sodium alginate were added, the Gel/SA/dECM bioink turned more
viscous as well as a little yellow compared to the dECM solution (inset), a white viscous liquid.
The steady viscosity of several bioinks was shown alginate has a greater effect on improving the viscosity of
in Figure 2C. Generally speaking, the viscosity of each the material than gelatin. Therefore, 5G3S1d, 6G3S1d, and
material decreased with the increase of shear frequency, 7G2S1d were selected as bioinks for printing scaffolds with
indicating that they were pseudoplastic fluids and shear consideration of both rheological properties test results
thinning fluids . The higher the material concentration, and pre-printing results.
[53]
the higher the fluid viscosity. In the test range shown in Han et al. prepared porcine liver dECM solution
[54]
the figure, the maximum viscosity of 7G2S1d was 182.93 and collagen solution with concentrations of 1.5% and 3%,
Pa, and the maximum viscosity of 4G2S1d was 15.91 Pa. respectively, for 3D-printed tissue-engineered scaffolds.
It was found that the higher the concentration was, the In the shear frequency range from 1 to 100 rad·s , the
−1
more stable the decrease rate of viscosity with the increase maximum storage modulus of the two bioinks were no
of shear frequency, indicating that scaffold constructed by more than 1000 Pa. Compared with their bioinks, the
the material with high concentration had a lower risk of viscoelasticity of bioinks in our study exhibited higher
deformation or collapse after 3D printing. viscoelasticity. In addition, during the shear rate range
Thixotropy is a reversible sol rheological phenomenon from 0 to 1000 s , the steady viscosity of the bioink with
−1
in which the viscosity and shear stress of the gel change sodium alginate in our study was also higher than that of
with time as a result of external forces such as oscillation, pure collagen solution. It is suggested that the addition of
agitation, and compression, reflecting the time dependence gelatin and sodium alginate, two high-viscosity materials,
of fluid viscosity. The area enclosed by the two curves formed can improve the stability and printability of bioink.
by the change of fluid shear stress as a result of the increase Compared with the dECM bioinks derived from porcine
and decrease of shear rate is called thixotropic ring. The fat, cartilage, and heart prepared by Pati et al. , the groups
[33]
larger the area of the thixotropic ring is, the stronger the of bioinks prepared in our study had higher viscoelasticity
time stability of the fluid is. As shown in Figure 2D–H, and steady viscosity. After gelatin and sodium alginate
the higher the bioink concentration was, the stronger the were added, Gel/SA/dECM bioink turned more viscous as
thixotropy was in general. The thixotropy of 6G3S1d was well as a little yellow (Figure 2I) compared to the dECM
stronger than that of 7G2S1d, possibly because sodium solution (Figure 2I inset), a white viscous liquid.
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2023) 117 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i1.630